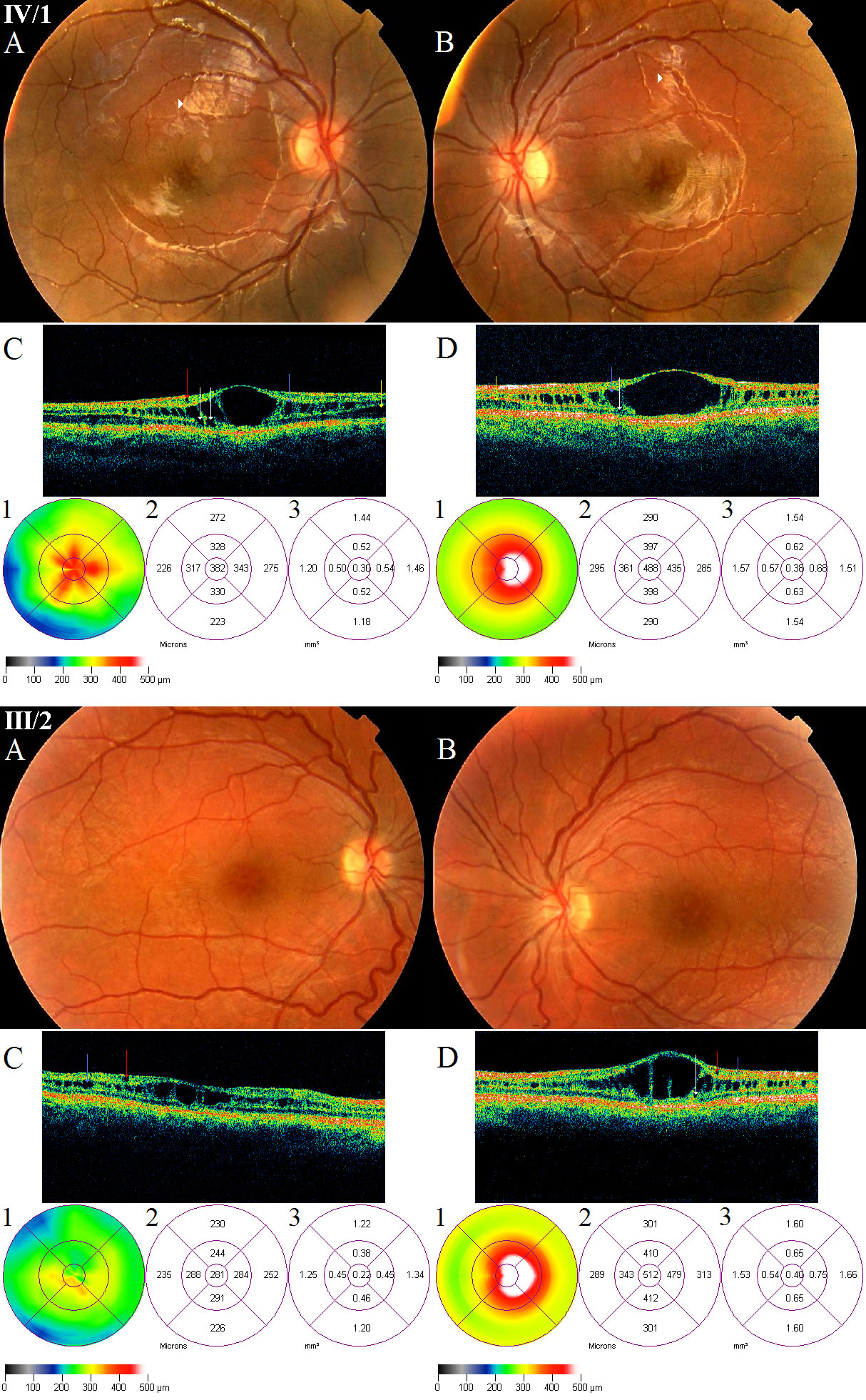
Figure 3. Fundus photographs and optical
coherence tomography images of patients IV/1 and III/2 suffering in
X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. In patient IV/1, the fundi show
radially oriented intraretinal foveomacular cysts in a spoke-wheel
configuration, with the absence of foveal reflex (IV/1 A, B). A
golden-yellow reflex called Mizou-Nakamura phenomenon is seen on the
posterior pole of both eyes of patient IV/1 marked by white arrowheads (A,
B). The OCT images of him (IV/1 C, D) reveal retinoschisis
in the inner nuclear layer (marked by blue arrow), in the photoreceptor
layer (marked by yellow arrow) and some cysts in the outer plexiform
layer (marked by white arrows) in both eyes, and one cyst in the
ganglion cell layer (marked by red arrow) in the right eye. His OCT
scans and foveal thickness maps show significant diffuse thickening of
the right fovea (IV/1 C, C1-2), and because of the huge central
cyst the significant pronounced thickening of the left fovea (IV/1 D,
D1-2) compared with the controls. The eccentric fixation is clearly
identifiable on his left FT map (IV/1 D1). In patient III/2, the fundi
show spoke-wheel configurations in the foveas with the absence of
foveal reflex (III/2 A, B). The OCT images reveal retinoschisis
in the inner nuclear layer (pronounced in the left eye), small cysts in
the ganglion cell layer of both eyes (III/2 C, D) and one cyst
in the outer plexiform layer of left eye (III/2 D). His OCT scans and
foveal thickness maps show significant diffuse thickening of the right
fovea (III/2 C, C1-2), and because of the huge central cyst the
significant pronounced thickening of the left fovea (III/2 D,
D1-2). The eccentric fixation is clearly identifiable on his left FT
map (IIII/2 D1).
![]() Figure 3 of Lesch,
Mol Vis 2008; 14:1549-1558.
Figure 3 of Lesch,
Mol Vis 2008; 14:1549-1558. 