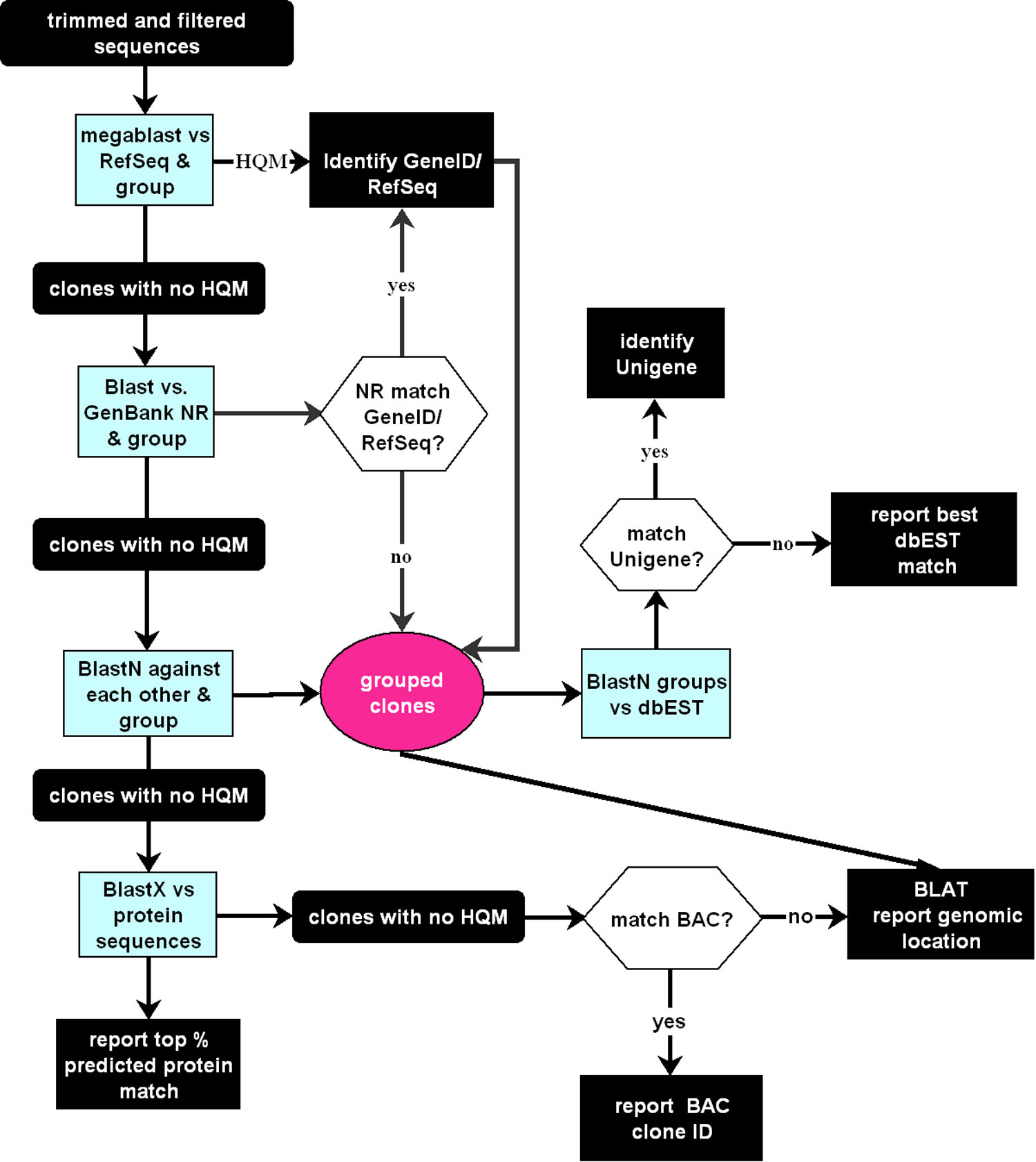
Figure 1. Flowchart for GRouping and
Identification of Sequence Tags (GRIST). High quality matches (HQM)
under our default conditions are at least a 97% identity over a minimum
length of 50 bp for NCBI RefSeq/NR (non-redundant) database matches and
96% identity over a minimum 100 bp length for NCBI dbEST database
matches. Blast matches against NR are filtered to ignore multigene
clones (such as bacterial artifical chromosomes [BACs]) and known
artifacts. NR matches are checked for GeneID and are grouped with
RefSeq matches for the same GeneID. This takes account of short or
incomplete RefSeqs. Unigenes are assigned independently by BLAST
against dbEST. UniGene assignments for the top eight HQM dbEST matches
for each clone are identified, and those that occur at frequencies of
at least 15% for the whole group are reported. This can help identify
Unigene problems, overlapping genes, and variant transcripts.
![]() Figure 1 of Wistow,
Mol Vis 2008; 14:1327-1337.
Figure 1 of Wistow,
Mol Vis 2008; 14:1327-1337. 