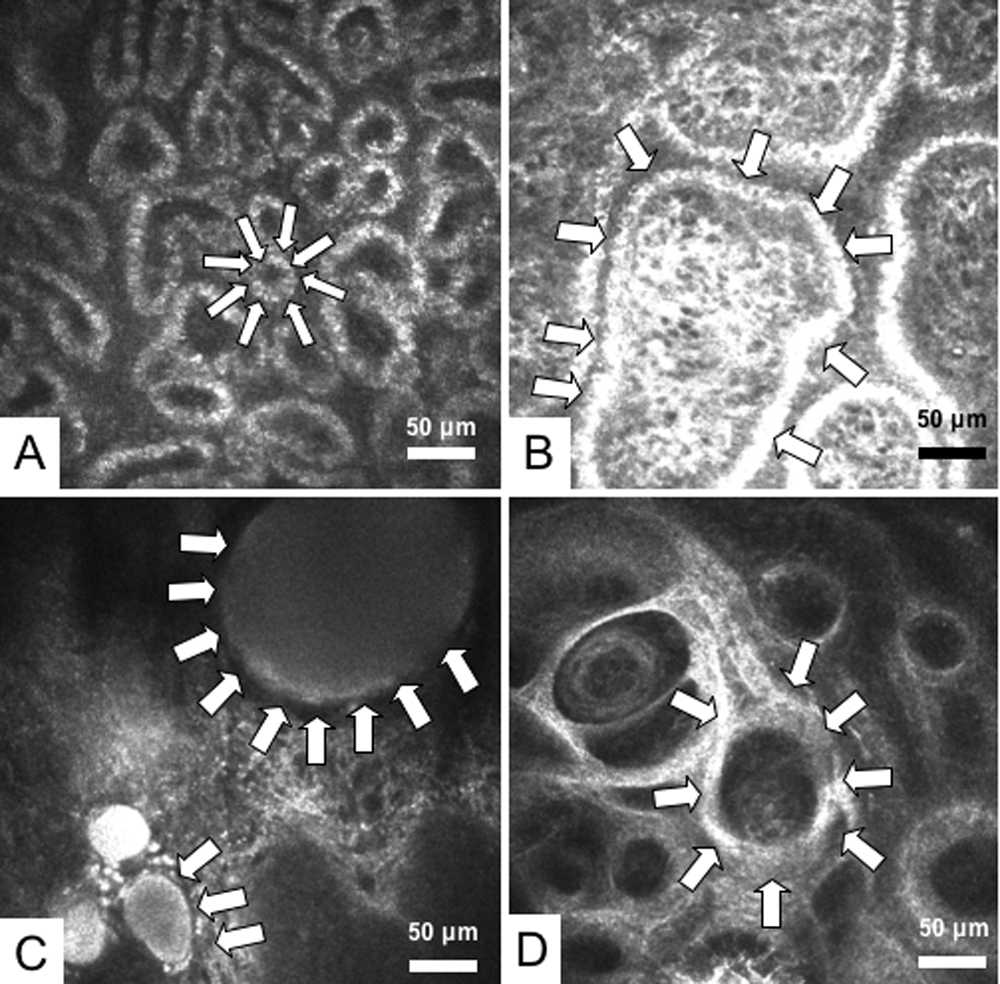
Figure 3. Meibomian gland (MG) images
observed by in vivo laser confocal microscopy. A: One of the MG
images from a representative 45-year-old male normal control subject is
shown. White arrows depict a typical acinar unit. Note the presence of
numerous and compact acinar units. Mean acinar unit densities and
diameters were calculated from a total of nine confocal images obtained
from the lower lid of the subject. The mean acinar unit density
calculated was 112/mm2, and the mean acinar unit diameter
was 46 μm. The diameter of the acinar unit depicted by the arrows is 35
μm. B: One of the representative MG images from a 66-year-old
female patient with MGD is shown. Note the enlargement of acinar unit
(outlined by white arrows) due to inspissation of meibum secretion. The
MG drop out grade was 1, and expressibility grade was 1. Mean acinar
unit densities and diameters were calculated from a total of nine
confocal images obtained from the lower lid of the subject. The mean
acinar unit density calculated from the overall images was 69/mm2,
and the acinar unit diameter was 72 μm. Note that acinar units might
show considerable enlargement. The diameter of the acinar unit depicted
by the arrows is greater than 250 μm. C: One of the
representative MG images from a 54-year-old female patient with MGD is
shown. The patient had advanced disease with grade 2 MGD and the meibum
secretion could not be expressed due to orifice obstruction (MG
expressibility grade 2). Note the remarkable dilatation of acinar units
with inspissation of meibum secretions (white arrows). D:
Representative MG image from a 78-year-old female patient with advanced
MGD is shown. The MG drop out grade was 2, and the MG expressibility
grade was 3. Note the atrophy in the glands with extensive
periglandular fibrosis (white arrows).
![]() Figure 3 of Matsumoto, Mol Vis 2008;
14:1263-1271.
Figure 3 of Matsumoto, Mol Vis 2008;
14:1263-1271. 