![]() Figure 8 of
Johnson, Mol Vis 2007;
13:887-919.
Figure 8 of
Johnson, Mol Vis 2007;
13:887-919.
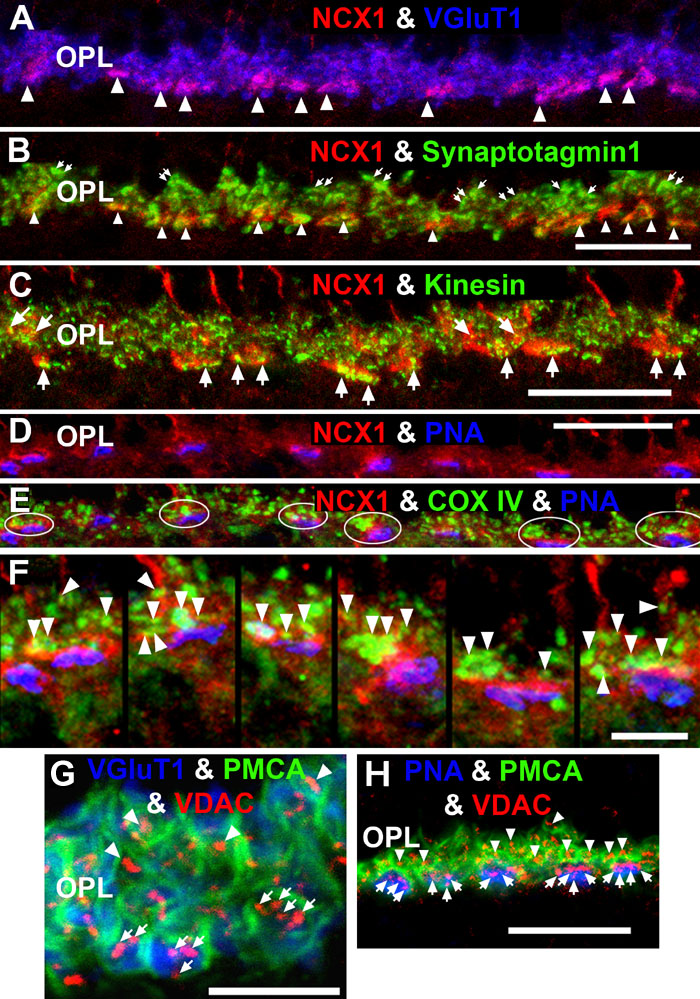
Figure 8. NCX1 localizes to ribbon synaptic units of cone pedicles and mitochondria closely associate with PMCA in photoreceptor terminals
A: NCX1-positive cone pedicles (red) and VGluT1 (blue) colocalize in the proximal ONL (white arrowheads: purple pixels). B: Synaptotagmin 1 (green) labels photoreceptor synaptic vesicles. Small NCX1- and synaptotagmin 1-positive puncta colocalize in rod spherules (white arrows: yellow pixels), while larger colocalized clusters are present in cone pedicles (white arrowheads: yellow-orange pixels). Scale bar equal 20 μm. C: Kinesin KIF3A (green) labels photoreceptor ribbons and docked synaptic vesicles. The kinesin-labeled rod spherules have an arc-shaped appearance and colocalize with diffusely located NCX1 (small yellow puncta). In contrast, cone pedicles have large clusters of double labeled NCX1- and kinesin-positive puncta (white arrows: yellow-orange pixels). Scale bar equal 20 μm. D-F: Mitochondria cluster away from the active zone in cone pedicles. Scale for D and E equal 20 μm and for F equal 10 μm. D: NCX1 (red) and PNA (blue) colocalize in cone pedicles (purple pixels). E: Triple labeling with NCX1, PNA and COX IV (green) reveals that the cone pedicles (white ellipsoids) contain multiple mitochondria that are located away from the ribbon synaptic unit. F: Higher magnification image of the same six pedicles in E reveals the COX IV and NCX1 colabeling (white arrowheads) and the distance of the COX IV-positive mitochondria from the active zone. G, H: Mitochondria closely associate with PMCA in the rod spherules and cone pedicles. Triple labeling with PMCA (green), VDAC (red), and with either VGluT1 (blue) or PNA (blue). Rods contain a single large mitochondrion (arrowheads) located close to the PMCA-labeled membranes. Cone pedicles contain multiple mitochondria (white arrows) clustered close to PMCA-labeled membranes, which are located away from the active zones. Scale bar equal 20 μm.