![]() Figure 6 of
Zhao, Mol Vis 2007;
13:873-880.
Figure 6 of
Zhao, Mol Vis 2007;
13:873-880.
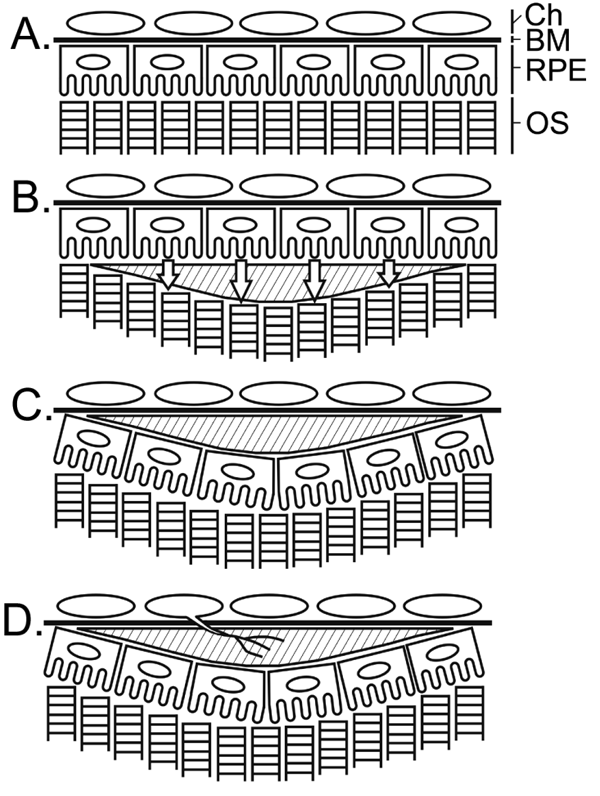
Figure 6. Schematic illustration of RPE translocation and sub-RPE deposit formation
A: Normal retina. B: A deposit (shade area) has formed in the subretinal space, which disrupts direct contact between photoreceptor outer segment (OS) and the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). RPE cells leave Bruch's membrane (BM) and migrate toward photoreceptors (indicated by open arrows). C: The cells then form a new layer between the deposit and photoreceptors to reestablish RPE-photoreceptor contact, resulting in RPE translocation. The deposit, originally in the subretinal space, becomes a sub-RPE deposit. D: Bruch's membrane devoid of RPE attachment is susceptible to invasion of new blood vessels from the choroid (Ch).