![]() Figure 5 of
Hunter, Mol Vis 2007;
13:431-442.
Figure 5 of
Hunter, Mol Vis 2007;
13:431-442.
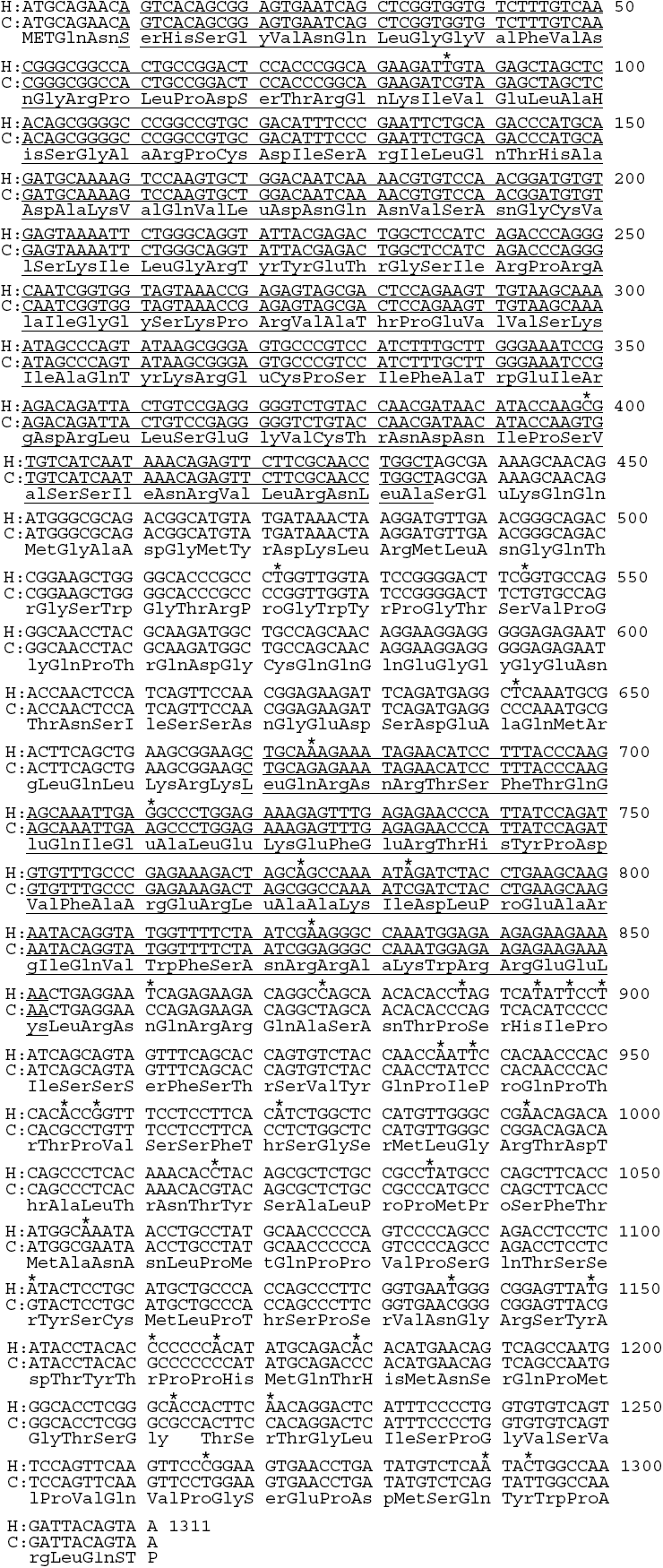
Figure 5. Comparison of the canine and human PAX6 coding sequence (CDS), and amino acid sequence
Human (NM_001604) CDS (first row); canine (EF141016) CDS (second row); corresponding amino acid sequence (436 aa; third row). The first underlined region is the paired domain (426 bp), followed by the linker region (234 bp). The second underlined region is the homeodomain (183 bp), followed by the PST domain (459 bp). The asterisks mark the 36 nucleotide differences between dog and man, two in the paired domain; three in the linker; five in the homeodomain; and 26 in the PST domain. Thirty-five of the 36 nucleotide differences occurred in the third position of the triplet codon, and did not alter the translated amino acid. Only one nucleotide difference occurred at the first position of a codon (base pair 1,213) resulting in an ACC (threonine) in man, and a GCC (alanine) in the dog. This change occurred in exon 12 which was part of the PST domain. As a result, the human and canine PAX6 nucleotide coding sequences were 97.3% identical, and the corresponding amino acid sequences were 99.8% identical.