![]() Figure 7 of
Xie, Mol Vis 2007;
13:397-407.
Figure 7 of
Xie, Mol Vis 2007;
13:397-407.
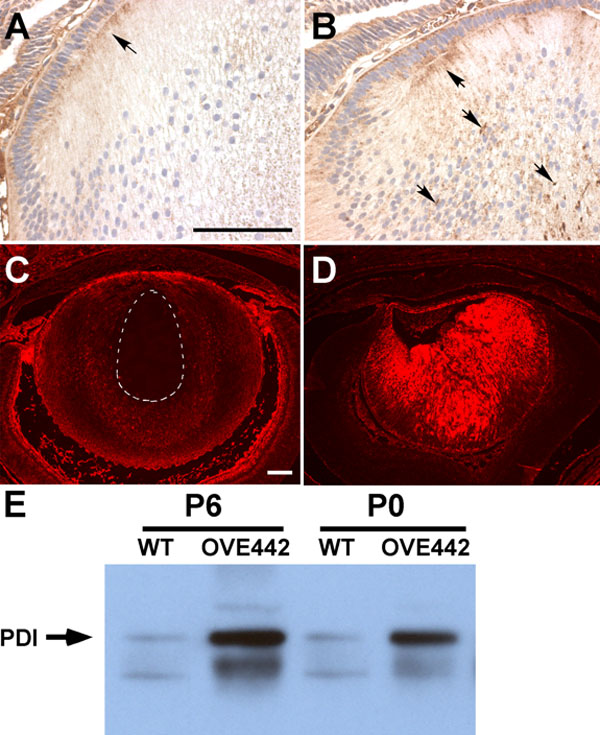
Figure 7. Detection of COX and PDI proteins
In the WT E18.5 lens (A), COX protein was detected in the epithelial cells and in the secondary fiber cells at the cortex. Strong COX-immunostaining was seen in the anterior tips of the secondary fiber cells (A, arrow). COX-staining was enhanced in the transgenic lens (B), particularly in the central region of the lens, where concentrated COX-staining was seen (B, downward arrows). PDI (rhodamine fluorescence in red) is highly expressed in the lens epithelial cells and cortical fiber cells in WT lens (C). PDI staining is lost in the central fiber cells (C, circled area). In contrast, PDI expression persists in all the lens fiber cells in OVE442 transgenic mice (D). E: PDI western blot analysis on newborn (P0) and postnatal day 6 (P6) lens. Compared to the PDI protein level in the WT lenses, expression is increased significantly in the OVE442 transgenic lenses (E, arrow). The lower band is from the reactivity of the secondary antibody to mouse endogenous immunoglobulin protein.