![]() Figure 1 of
McMahon, Mol Vis 2007;
13:258-272.
Figure 1 of
McMahon, Mol Vis 2007;
13:258-272.
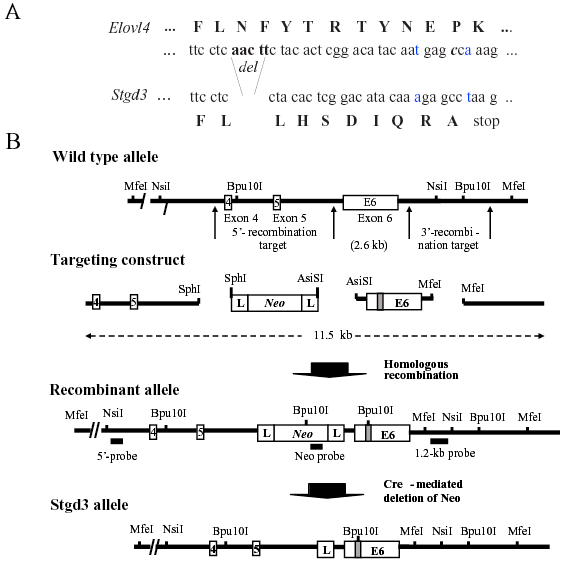
Figure 1. Gene-targeting strategy for generation of Stgd3-gene knockin mice
A: Partial nucleotide sequence from exon 6, and the encoded amino acids (capital letters), of the wt (Elovl4) and mutant (Stgd3) alleles. Shown are the mutations introduced into the Elovl4 sequence prior to assembly of the targeting construct. Five nucleotide base pairs, corresponding to those absent in Stargardt-3 patients, were deleted (del). Two point mutations (the altered and substituted nucleotides are shown in blue) were introduced in the sequence downstream of the deletion to generate a new C-terminal sequence that is identical to that found in STGD3 patients. B: Schematic maps of a portion of the Elovl4 allele encompassing exons 4, 5, and 6, the targeting construct, recombinant allele and the final Stgd3 allele. Restriction sites used for cloning and for Southern blot verification of recombination and deletion events, as well as the location of the Southern probes are included. Mutations in exon 6 are shown schematically as a shaded box, within which the new Bpu10I restriction site introduced during sequence manipulation is shown. Homologous recombination of the 11.5-kb targeting construct generates a recombinant allele containing exon 6 with the Stgd3 mutation, a neomycin selection cassette (Neo) flanked by lox P sites (L), and 4.2 kb and 3.1kb of 5'- and 3'-targeting sequence, respectively. Breeding of recombinant Neo/wt mice with Cre-transgenic mice leads to Cre-mediated deletion of the Neo cassette and generation of the mice carrying the final Stgd3 allele.