![]() Figure 1 of
Camelo, Mol Vis 2007;
13:2263-2274.
Figure 1 of
Camelo, Mol Vis 2007;
13:2263-2274.
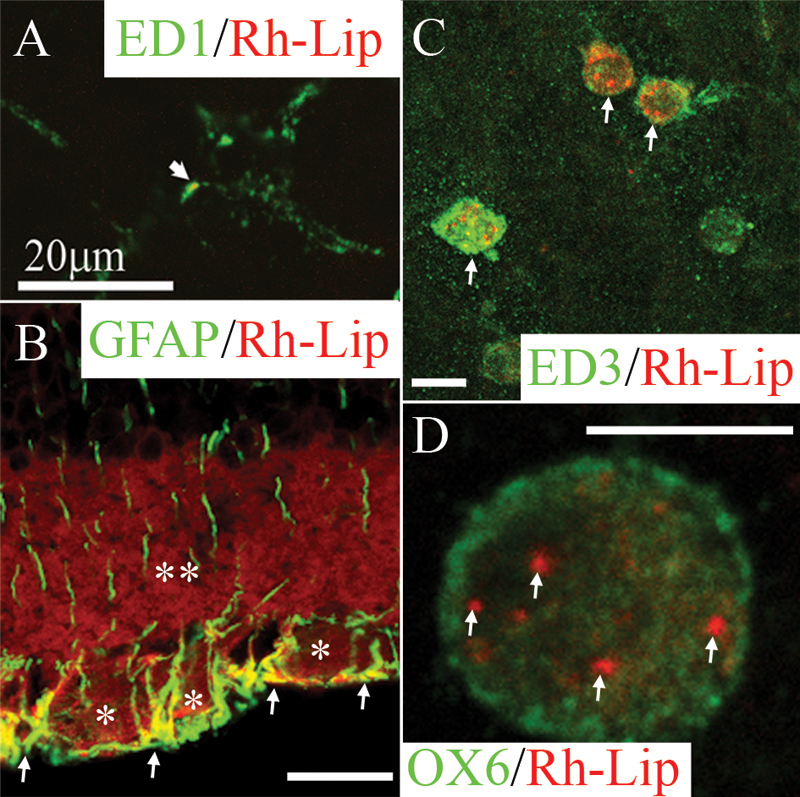
Figure 1. Biodistribution and phenotype of cells internalizing rhodamine-conjugated liposomes in the retina and vitreous of normal rats 24 h post IVT injection of Rh-Lip
A: On a whole-mounted retina, some microglial cells stained with ED1 (green) are detected phagocytosing limited number of rhodamine-conjugated-liposomes (Rh-Lip, red). B: rhodamine-conjugated-liposomes (Rh-Lip, red) are internalized by GFAP-positive (green)-retinal Müller glial cells as evidenced by colocalization (yellow) in the internal limiting membrane and the ganglion cell layer. Fluorescent Rh-Lip are seen as red fluorescent round dots on the images while free rhodamine is detected as diffuse red fluorescence within the ganglion cell layer (an asterisk) and inner plexiform layer (a double asterisk). C: On a whole-mounted retina, macrophages expressing ED3 (green) located at the level of the inner limiting membrane of the retina internalized Rh-Lip injected into the vitreous. D: Some of these macrophages express OX6 (green) suggesting they are activated and contain various amount of Rh-Lip. D shows a single OX6-positive macrophage containing a few Rh-Lip located into its cytoplasm. Photographs are representative of images obtained from frozen sections (B) and whole mounts (A, C, and D) performed on a total of 12 eyes. All bars represent 20 μm except in D (10 μm). Confocal optical section, in all images, is 3 μm.