![]() Figure 3 of
Hogewind, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1793-1801.
Figure 3 of
Hogewind, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1793-1801.
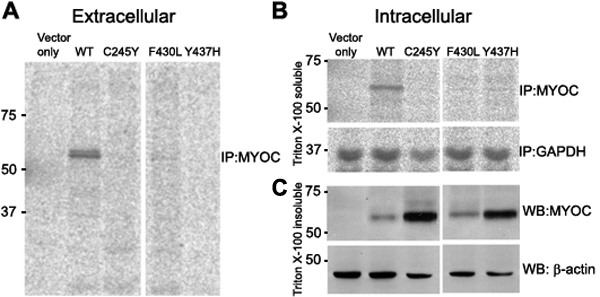
Figure 3. Functional characterization of the p.Phe430Leu mutation in Myocilin
A: Immunoprecipitation assay is used to monitor secretory properties of Myocilin. Lane 2 is the wild type protein and lane 4 is the mutant protein for p.Phe430Leu. Lanes 3 and 5 contain two reported mutations (p.Cys245Tyr and p.Tyr437His, respectively) that are used for comparison. Note the lack of secretion for all three mutant proteins compared to the wild type. B: Immunoprecipitation for the Triton X-100 soluble fraction of intracellular Myocilin is illustrated. Note the absence of the mutant proteins in this fraction compared to the wild type. GAPDH is the housekeeping protein for loading reference. C: Western blotting was used to detect Myocilin in the Triton X-100 insoluble fraction. Note the abundance of all three mutant proteins compared to the wild type. β-Actin is the housekeeping protein for loading reference. CHO-K1 cells were used to express wild type and mutant MYOC proteins. The loading order of the gel was identical in all three panels: lane 1, vector only; lane 2, wild type Myocilin protein; lane 3, p.Cys245Tyr mutant Myocilin; lane 4, p.Phe430Leu mutant Myocilin (this study); and lane 5, p.Tyr437His mutant Myocilin. The single letter amino-acid codes are used in the figure due to lack of space. The numbers on the left-hand side of each panel denote the molecular weight range. This figure shows that the p.Phe430Leu mutation diminishes the secretory properties of Myocilin and makes it highly insoluble in Triton X-100.