![]() Figure 3 of
Jiang, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1783-1792.
Figure 3 of
Jiang, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1783-1792.
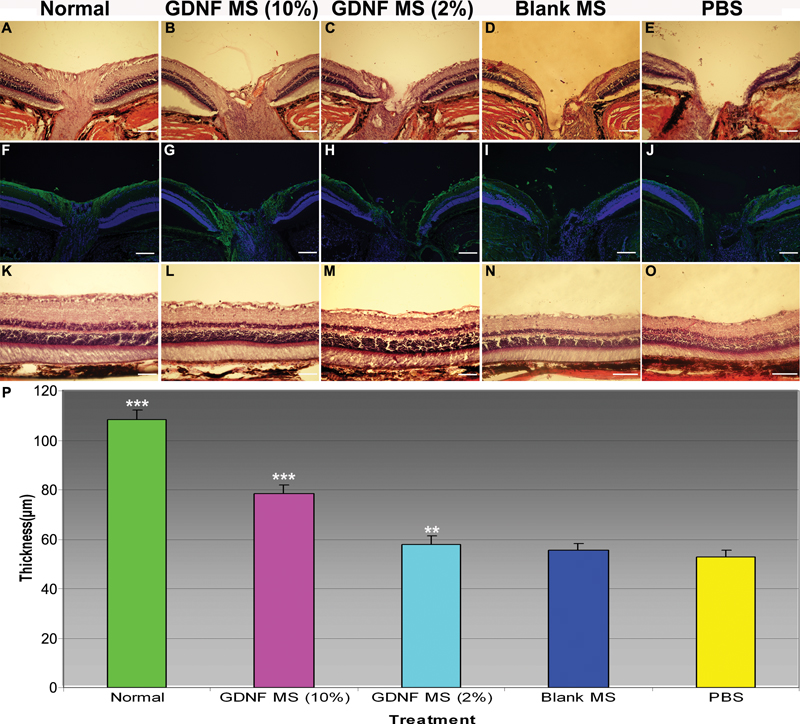
Figure 3. GDNF microspheres reduce retinal damage due to chronic intraocular elevation
A-E Chronic IOP elevation resulted in the cupping of the ONH (upper and middle row, scale bar: 200 μm): A shows the normal ONH architecture. Ten percent of GDNF microsphere (MS) treatment (B) reduced the ONH excavation, and 2% GDNF MS treatment (C) moderately reduced the ONH excavation compared with blank MS treatment (D) and PBS (E). F-J (Neurofilament 200 kDa, middle row): F also illustrates the normal ONH architecture. Ten percent of GDNF MS treatment (G) decreased the loss of NFL, and 2% GDNF MS treatment (H) moderately decreased the loss of NFL compared with blank MS treatment (I) and PBS treatment (J). K-O Effects of GDNF MS treatment on preservation of the thickness of IPL after chronic IOP elevation (lower row, scale bar: 100 μm): K shows the normal retinal architecture. Ten percent of GDNF MS treatment (L) resulted in the preservation of the thickness of IPL, and 2% GDNF MS treatment (M) moderately resulted in a protection of IPL compared with blank MS (N) and PBS treatment (O). (P) shows the quantitative analysis of GDNF MS treatment on the thickness of IPL. Chronic IOP elevation resulted in a significant loss of the thickness of IPL compared with that of the normal retina (p<0.001). Ten percent of GDNF MS treatment resulted in a significant reservation of the thickness of IPL compared with 2% GDNF MS, blank MS, and PBS treatment (p<0.001). Two perecent of GDNF MS treatment resulted in significant reservation of the thickness of IPL compared with PBS treatment (p<0.01). There were no significant differences between groups treated with 2% GDNF MS versus blank MS nor between groups treated with blank MS versus PBS (p>0.05). Three asterisks indicate p<0.001 and a double asterisk denotes p<0.01. In the figure, MS represents microsphere.