![]() Figure 3 of
Bai, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1589-1600.
Figure 3 of
Bai, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1589-1600.
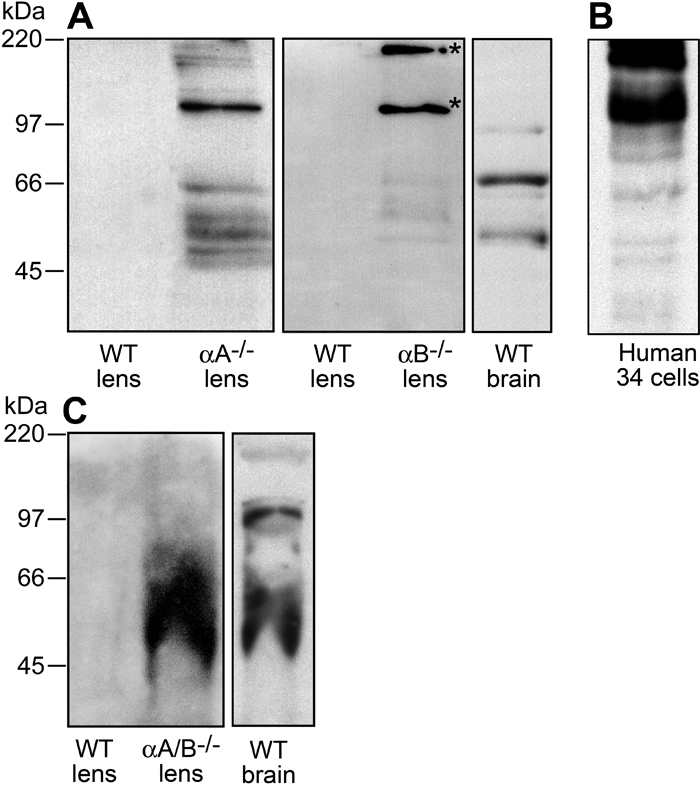
Figure 3. Immunoblot analysis of tau in mouse lens
Lens cortical fiber cell MAPs from 8-month-old wild type, αA-/-- and αB-/-- mice were prepared and the proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. Tissue from 16 to 20 lenses was pooled for each preparation. Samples were heated to 95 °C in SDS-PAGE sample buffer to detect tau in lens samples. Immunoblot analysis was performed with the monoclonal antibody KAM-MA305 to full length brain tau protein and the Tau-5 antibody which reacts with nonphosphorylated as well as phosphorylated forms of tau. A: Antibody used was KAM-MA305 to full length brain tau. Left panel, Wild type (WT) and αA-/-- MAPs. Tau was undetectable in the wild type lenses, but tau immunoreactive proteins were detected in the 45-66 kDa range in the αA-/-- and αB-/-- lens fractions. Note that the αA-/-- tau immunoreactive bands included a prominent 100 kDa band; middle panel, WT and αB-/-- MAPs. Tau immunoreactivity was undetectable in the wild type MAPs from cortical fiber cells, but higher molecular weight crosslinked bands (asterisks) crossreacted with the antibody in the αB-/-- MAPs. Right panel, Microtubule associated proteins were isolated from 3-month-old mouse brains and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Note that the major immunoreactive bands were detected at 45-66 kDa, whereas minor bands were detected at about 100 kDa. B: Human cells-34 lysates were analyzed with the KAM-MA305 antibody. Tau immunoreactive bands at about 100 and 200 kDa bands were prominent in these cells. C: Antibody used was the Tau-5 antibody which recognizes both nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated forms of tau; left panel, Immunoreactivity of wild type and αA/B-/-- lens fractions. Although no immunoreactive bands were detected in the wild type lens, a broad band was observed in the αA/B-/-- lens; right panel, wild type brain fractions run on the same gel with a similar broad band showing immunoreactivity to this antibody.