![]() Figure 2 of
Bagiyeva, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1458-1468.
Figure 2 of
Bagiyeva, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1458-1468.
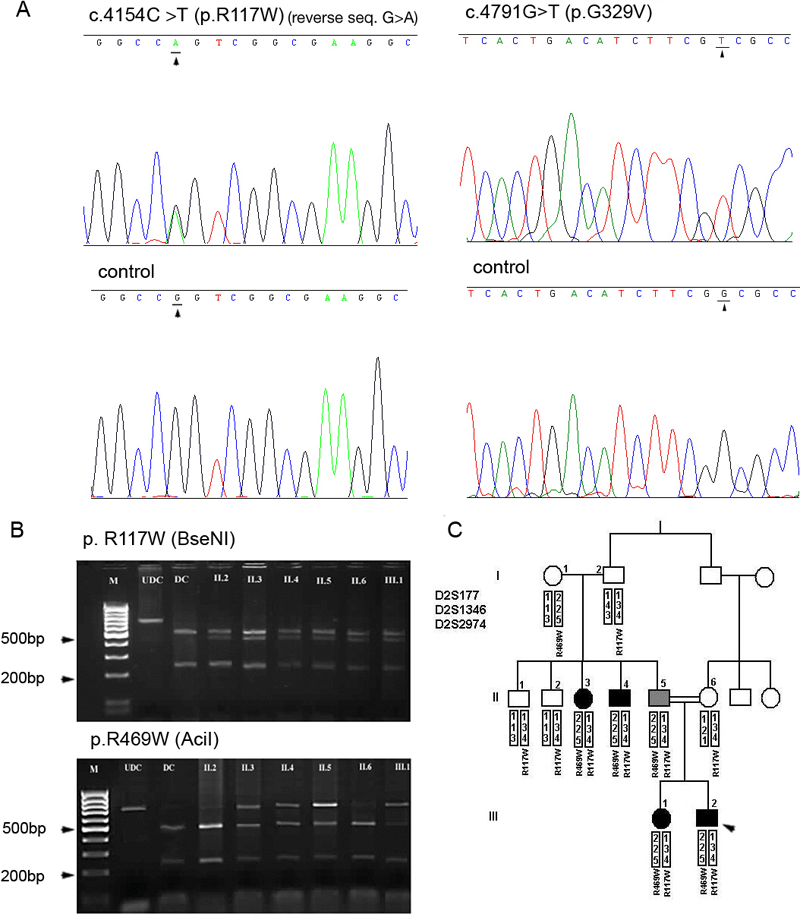
Figure 2. Newly detected mutations in families PCG9 and PCG21
A: Electropherograms of the DNA sequence from two patients, one from family PCG9 showing the mutation c.C4154T (causing the R117W substitution) in heterozygous state, and the other from family PCG21 showing the homozygous c.C4791T mutation (causing the G329V substitution). Note that the c.C4154 mutation is read in the complementary reverse sequence as a G>A substitution. B: Cosegregation analysis of the R117W and R469W mutations in the consanguineous family PCG9 by RFLP. UDC- and DC-undigested and digested PCR product from control DNA, respectively. C: Haplotype analysis of the CYP1B1 flanking markers in the PGC9 pedigree. II5 is a nonpenetrant obligated carrier (symbol in grey). The proband, III2, is indicated by an arrowhead.