![]() Figure 1 of
Lin, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1203-1214.
Figure 1 of
Lin, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1203-1214.
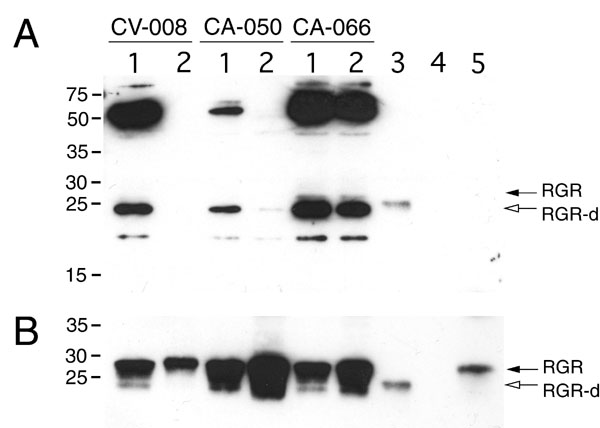
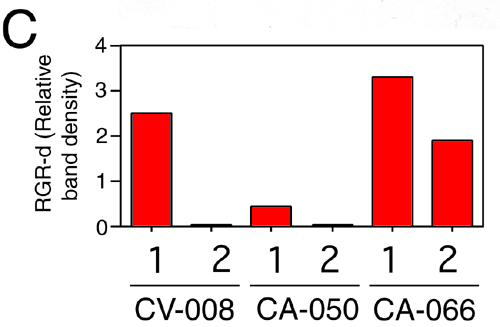
Figure 1. Western immunoblot assay of retinal G protein-coupled receptor splice isoform and retinal G protein-coupled receptor in human retina and retinal pigment epithelium
A: The expression of retinal G protein-coupled receptor splice isoform (RGR-d) in the neural retina (lane 1), and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE; lane 2) from donors CV-008 (73/F), CA-050 (73/F), and CA-066 (59/M) was analyzed on western blots using the DE17 antibody. B: The blot shown in A was stripped of bound antibodies and incubated subsequently with the HRGR-DE7 antibody. C: Relative level of RGR-d in reference to the amount of RGR. Initially, samples were loaded onto the gel so that RGR would be about equal intensity in each lane. The relative density of RGR-d bands (A) was then normalized to the band density of RGR (B). Controls included RGR-d baculovirus-transduced Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) whole cell extract (lane 3), and an equal amount of control Sf9 whole cell extract (lane 4). Human RGR protein (lane 5) was solubilized in 1% Triton X-100/PBS and isolated from RPE cells of a single donor (CA-014, 84-year-old female) by an immunoaffinity procedure [23]. Monomer RGR-d (open arrows) and full-length RGR (solid arrows) were detected by chemiluminescence using (A) SuperSignal West Femto and (B) ECLTM substrate systems. Donor CA-066 was diagnosed with retinal degeneration and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.