![]() Figure 2 of
Swain, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1114-1120.
Figure 2 of
Swain, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1114-1120.
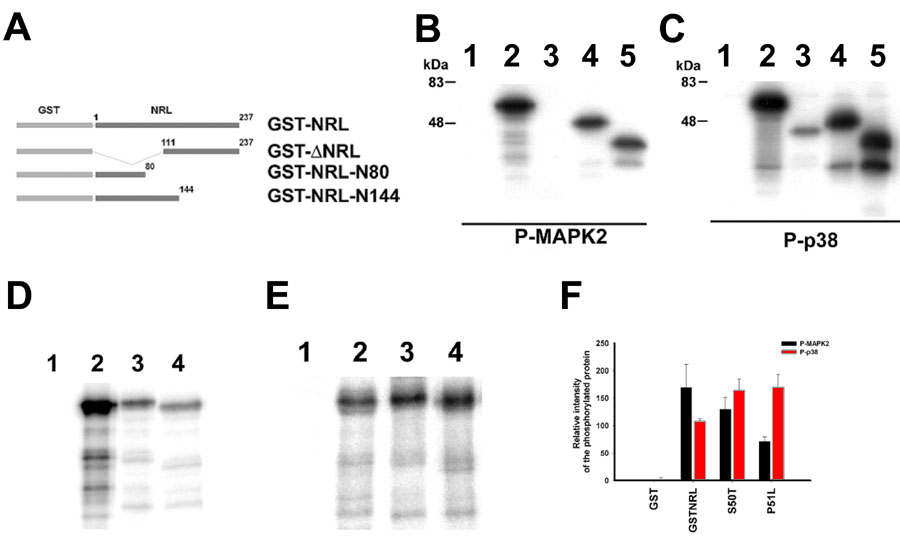
Figure 2. MAPKs produce differential phosphorylation of neural retina leucine-zipper and mutated neural retina leucine-zipper in vitro
A: Schematic representation of full length and truncated NRL expressed as GST-fusion protein and used as substrate in the phosphorylation assays. GST-NRL represents the fusion protein expressing the full length NRL; GST-DNRL, with carboxyl terminal 110 amino acids; GST-NRL-N144, with amino terminal 144 amino acids and GST-NRL-N80, with amino terminal 80 amino acids of NRL, respectively. Kinase-dependent phosphorylation assays were performed to phosphorylate full length and truncated GST-NRL using either (B) purified activated MAPK2 or (C) activated p38a in vitro. Radiolabeled proteins: Lane 1, GST; lane 2, GST-NRL; lane 3, GST-DNRL; lane 4, GST-NRL-N144; lane 5, GST-NRL-N80 were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. In similar studies, either (D) activated MAPK2 or (E) activated p38a was used to phosphorylate GST-NRL with or without specific mutations in vitro. Radiolabed samples analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography includes: Lane1, GST; lane 2, GST-NRL; lane 3, GST-NRL-S50T, lane 4, GST-NRL-P51L in the phosphorylation assay. The specific radioactivity of the protein was estimated by normalizing radioactivity with intensity of the corresponding protein band stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (F) Three independent experiments phosphorylated using similar conditions were used to estimate the relative changes in the radioactivity of the protein. Error bars represent the standard deviation, n=3 in the histogram.