![]() Figure 4 of
Matsuoka, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1058-1065.
Figure 4 of
Matsuoka, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1058-1065.
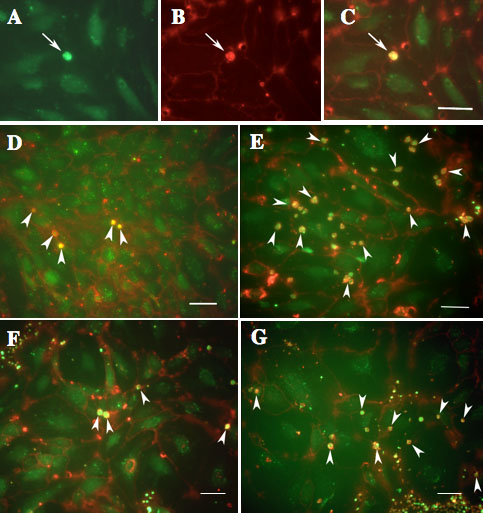
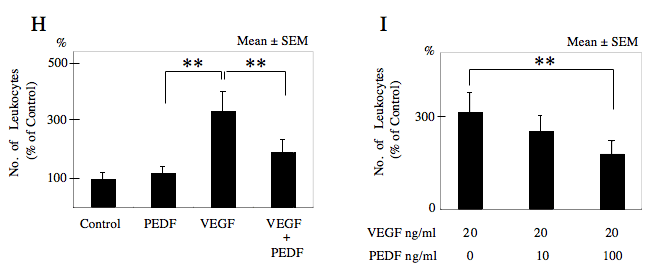
Figure 4. Confocal fluorescence microscopy for detection of adherent monocytes to human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Monocytes and nuclei of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were labeled in green with Calcein-AM (A). The cell surfaces of the monocytes and HUVECs were labeled red with rhodamine-conjugated Con-A lectin (B). Adherent monocytes appeared yellow in the merged images obtained by combining FITC and rhodamine images (C). Arrows show monocytes. D-G show merged images of HUVECs and adherent monocytes. HUVECs were treated with phosphate buffered saline as a control (D), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF; E), pigment epithelial growth factor (PEDF; F), and both VEGF and PEDF (G). H shows quantification of adherent monocytes. Administration of PEDF did not significantly alter the number of adherent monocytes compared to that of controls. Alternatively, when VEGF was added, the number of adherent monocytes was significantly increased (p<0.01). On the other hands, when PEDF was jointly administered with VEGF, the increase of adherent monocytes induced by VEGF was significantly reduced (p<0.01). I shows the effects of PEDF on adherent monocytes induced by VEGF. PEDF appeared to inhibit the increase of adherent monocytes induced by VEGF in dose dependent manner. Results represent the average of eight experiments±SEM. The data were analyzed by ANOVA with Fisher's LSD. Double asterisks indicate p<0.01.