![]() Figure 5 of
Qi, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1-11.
Figure 5 of
Qi, Mol Vis 2007;
13:1-11.
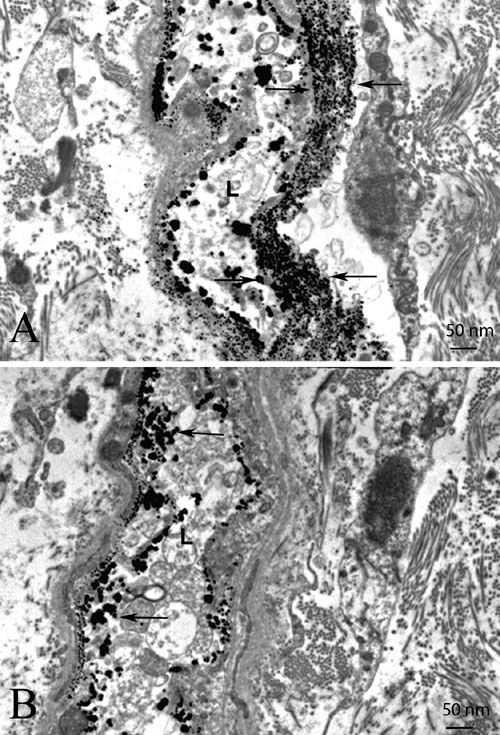
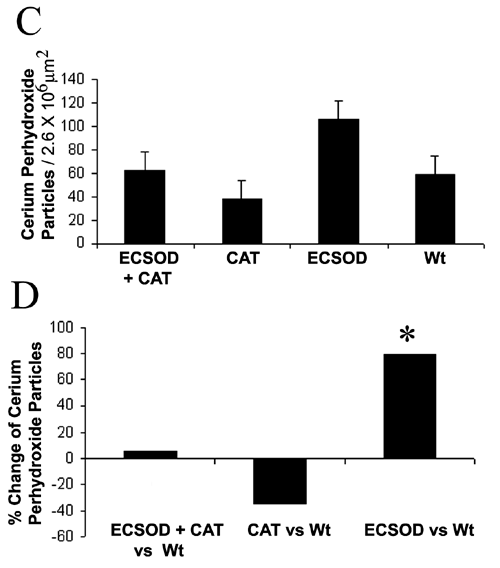
Figure 5. Reactive oxygen species in the optic nerve
Transmission electron micrographs show electron dense cerium perhydroxide (arrows) formed by the reaction of cerium chloride and endogenous hydrogen peroxide is more prominent in the optic nerves of animals protected by ECSOD (ECSOD OS; A) relative to unprotected nerves (Wt OS; B). The barplot shows mean cerium perhydroxide particle counts in the retrobulbar optic nerves protected by ECSOD and catalase (ECSOD OD), catalase (Wt OD), ECSOD (ECSOD OS) or unprotected EAE (Wt OS; C). Barplot (D) illustrates the relative changes in H2O2 reaction product counts in nerves treated with ECSOD and catalase, catalase or ECSOD relative to the unprotected nerves. Asterisk (*) represents p<0.05, L represents lumen.