![]() Figure 4 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2006;
12:821-831.
Figure 4 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2006;
12:821-831.
Figure 4.
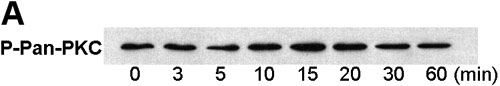
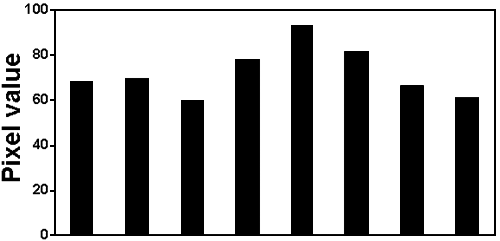
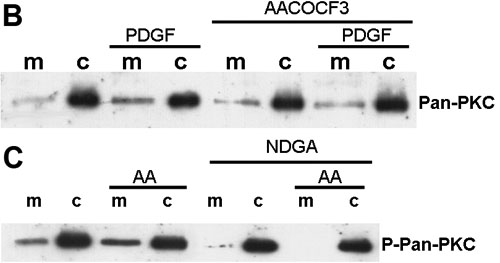
PDGF-induced PKC activation and translocation. A: For PKC activation, the cells (1.6 million) were gradually serum starved by incubating in 2% PBS medium overnight and then in serum free medium for 30 min before stimulating with 1 ng/ml PDGF for 0, 3, 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, and 60 min. The cell lysate at each time was then used for western blot analysis for the presence of activated or phosphorylated pan-PKC (P-PKC), using anti pan-P-PKC antibody. B: The effect of cPLA2 inhibitor on PDGF-induced PKC translocation. HLE cells (2 million) were serum starved 24 h and then preloaded with 20 μM cPLA2 (AACOCF3) inhibitor for 60 min followed by PDGF (20 ng/ml) stimulation for 30 min. The presence of pan-PKC was examined (probed with anti-pan-PKC antibody) in membrane and cytosolic fractions isolated from cells with and without PDGF stimulation, and from AACOCF3-pretreated cells with and without PDGF stimulation. The amount of proteins used for the gel was 5 μg and 2 μg from membrane fraction and cytosolic fraction, respectively. Cells without PDGF stimulation were used as the control. Two separate experiments were carried out and a typical pattern is shown. C: Exogenous AA-stimulated PKC translocation: cells (1.6 million) were serum starved 24 h before use. The cells were stimulated with and without 60 μM AA for 30 min and lysed. Membrane and cytosolic fractions were isolated and used for western blot analysis for the presence of pan PKC, using anti-pan PKC antibody. Some cells were preloaded 60 min with 10 μM of a specific inhibitor for lipoxygenase (NDGA) before AA stimulation. In all experiments, cells without AA stimulation were used as controls. The amount of proteins used for the gel was 5 μg and 2 μg from membrane fraction and cytosolic fraction, respectively. Two separate experiments were carried out and a typical pattern is shown.