![]() Figure 3 of
Zhao, Mol Vis 2006;
12:15-25.
Figure 3 of
Zhao, Mol Vis 2006;
12:15-25.
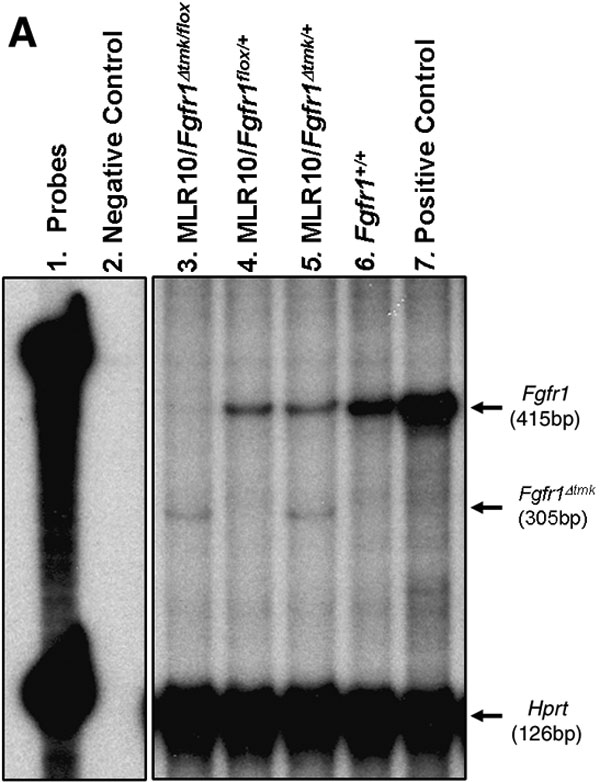
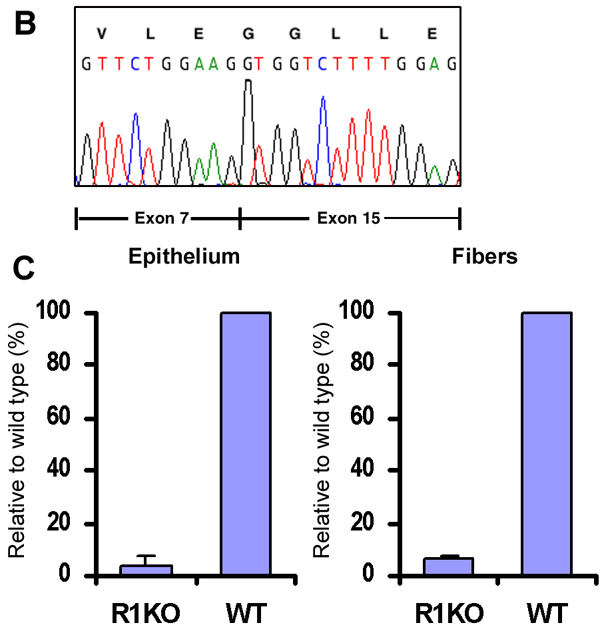
Figure 3. Lens-specific inactivation of Fgfr1 by MLR10 transgenic mice
A: An RNAse protection assay using an Fgfr1 cDNA probe spanning exons 14 to 16 detected a 415 bp protected fragment indicative of the wild-type Fgfr1 transcript in whole embryo E15.5 total RNA (lane 7), in adult lens total RNA from wild-type (lane 6), and in adult lens total RNA from heterozygous animals (lanes 4 and 5). In lens RNA from MLR10/Fgfr1Δtmk/+, an additional 305 bp protected fragment was detected, which indicated alternative splicing of the Fgfr1Δtmk allele (lanes 3 and 5). In lens RNA from MLR10/Fgfr1Δtmk/flox mice, the wild-type transcript was absent indicating the floxed allele of Fgfr1 was recombined efficiently by Cre recombinase (lane 3). B: Sequencing of the PCR-amplified smaller transcript revealed an alternative transcript where exon 7 was spliced onto exon 15 because of the deletion of genomic sequence spanning exon 8 through exon 14 in the Fgfr1Δtmk allele. C: Quantitative real time-PCR analysis of Cre-mediated Fgfr1 inactivation in the lens epithelial and fiber cells. In the lens epithelium of MLR10/Fgfr1flox/flox mice, the level of Fgfr1 transcripts was only 3.87% that of the wild type lens epithelium. Similarly, lens fiber cells from MLR10/Fgfr1Δtmk/flox mice only retain 6.11% of Fgfr1 transcripts relative to wild type lens fibers. Error bars represent the standard deviation present in samples analyzed in triplicate.