![]() Figure 4 of
Tetreault, Mol Vis 2006;
12:1699-1705.
Figure 4 of
Tetreault, Mol Vis 2006;
12:1699-1705.
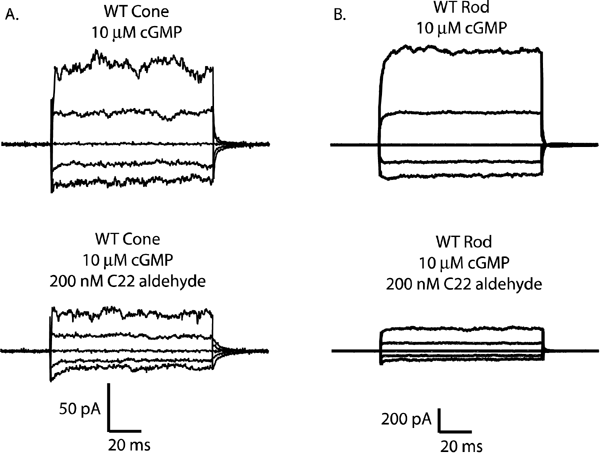
Figure 4. The wild-type cone and rod channels can also be inhibited by C22 aldehyde
Raw traces represent families of cGMP-activated currents in response to voltage steps ranging from -100 mV to +100 mV in 50 mV increments from a holding potential of 0 mV. Currents measured in the absence of 3',5'-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) were subtracted from all traces. A: Wild-type human cone CNGA3 channel in 10 μM cGMP in the presence and absence of 200 nM C22 aldehyde. Current was reduced by 53%. B: Wild-type bovine rod CNGA1 channel in 10 μM cGMP in the presence and absence of 200 nM C22 aldehyde. Current was reduced by 76%. Each patch was allowed to reach steady state after addition of the retinoid.