![]() Figure 3 of
Linberg, Mol Vis 2006;
12:1674-1686.
Figure 3 of
Linberg, Mol Vis 2006;
12:1674-1686.
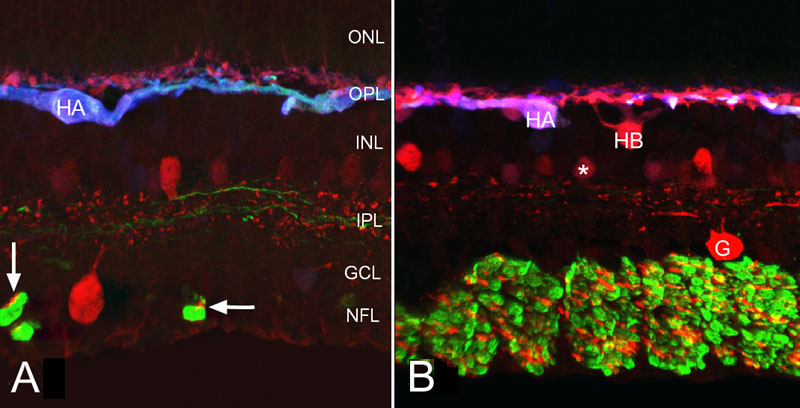
Figure 3. Confocal micrographs of triple labeled cat retina
Confocal micrographs of cat retina triple labeled with antibodies to calretinin (red), neurofilament (green) and calbindin D (blue). A: Normal cat retina. Two red, anti-calretinin-positive neurons lie on either side of the inner plexiform layer (IPL). An axonless HC (HA), labeled by all three probes, appears blue in this image, while the other HCs strongly labeled with anti-calretinin and less so with anti-calbindin D, remain reddish. Anti-neurofilament labeling is also evident in the nerve fiber layer (NFL) and processes running in the middle and outermost layers of the IPL. Note the anti-calretinin-positive fibers (arrows) in these fiber bundles. ONL represents outer nuclear layer; INL represents inner nuclear layer; GCL represents ganglion cell layer. B: Normal cat retina. Closer to the optic nerve head, the nerve fiber bundles are much larger than in A; a minority of these fibers lack neurofilament protein, but are anti-calretinin-positive. An anti-calretinin-positive ganglion cell (G) sends processes into the middle of the IPL. Two amacrine cells in the INL are brightly labeled with anti-calretinin; AII amacrine cells (*) stain less intensely with this antibody. The axonless HC (HA), labeled by all three probes, has a light violet hue; the cell body of the axon-bearing type (HB) and its dendrites remain red. The perikaryon of the B-type HC lies deeper in the INL than does the more planar HA type. B is reprinted from Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, 24, S. K. Fisher, G. P. Lewis, K. A. Linberg and M. R. Verardo, "Cellular remodeling in mammalian retina: results from studies of experimental retinal detachment," 395-431, 2006, with permission from Elsevier.