![]() Figure 1 of
Andrieu-Soler, Mol Vis 2006;
12:1334-1347.
Figure 1 of
Andrieu-Soler, Mol Vis 2006;
12:1334-1347.
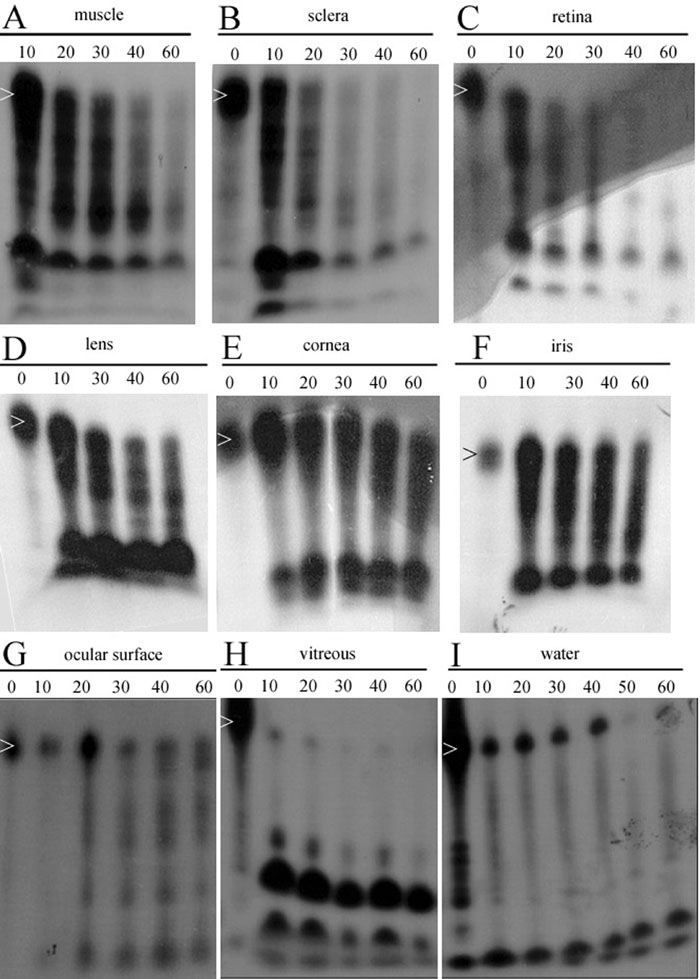
Figure 1. Degradation rate of a 53-mer ribozyme in mouse ocular tissues after application to the ocular surface
Ten week-old C57Bl6 mice were used for these experiments. After sacrifice, eyes were enucleated, tissues (cornea, iris, lens, ocular muscles, retina/choroid, and vitreous) were dissected and collected. Then 1.7-2 pmol of 32P-labeled ribozymes were mixed with the tissues or in bidistilled water at 37 °C for different periods of time (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 min, n=4 per timepoint). To evaluate the degradation rate of nucleic acids in vivo, 2 pmol (in 20 μl) of radiolabeled ribozymes were instilled on the eye surface of anesthetized mice (n=2 per timepoint). At various timepoints after instillation the eye surface was rinsed with 120 μl of bidistilled water and collected. The ribozymes were then extracted as described in reference [73] for the extraction of ODNs from ocular tissues, and their migration was observed on denaturating acrylamid gel. 32P-labeled ribozymes were mixed with muscle (A), sclera (B), retina (C), lens (D), cornea (E), iris (F), ocular surface (G), vitreous (H), or water (I) at 37 °C for different periods of time: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 min, n=4 per timepoint. White arrows indicate full length ribozyme.