![]() Figure 5 of
Taliana, Mol Vis 2006;
12:1233-1242.
Figure 5 of
Taliana, Mol Vis 2006;
12:1233-1242.
Figure 5.
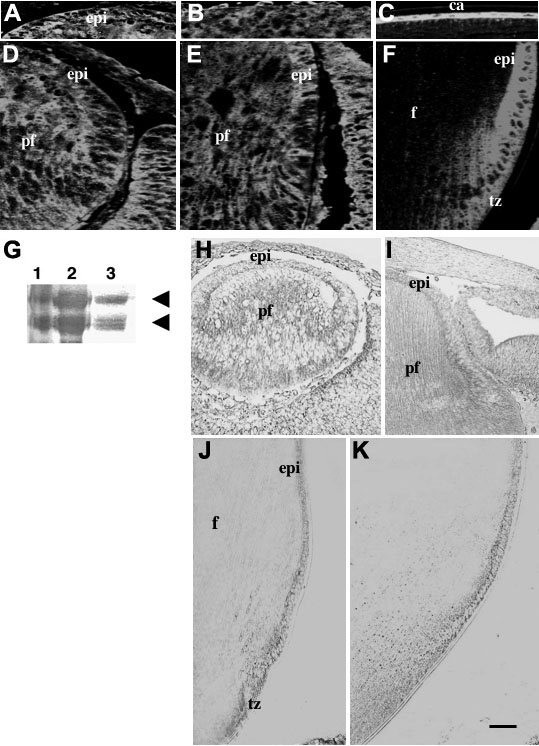
Localization of vitronectin during embryonic and postnatal rodent lens development. A-F: Immunofluorescent localization of vitronectin in mouse eyes. A and D: At embryonic day 12.5 (E12.5), patchy vitronectin reactivity is detected in both differentiating epithelia and primary fiber cells. B and E: At E17.5, vitronectin reactivity is weaker in the primary fibers but stronger in the epithelium (B). C and F: At postnatal day 21 (P21), vitronectin reactivity is clearly restricted to the epithelium and early fiber differentiation in the transitional zone. G: Western blotting of P21 rat capsule lysates with a vitronectin-specific antibody. Reactive bands were detected at about 70 kDa and 65 kDa (arrows) that matched the positive control (purified vitronectin). The vitronectin molecule typically denatures readily (as with boiling in this case), to produce these distinctive bands. Lanes are as follows: 1. molecular weight markers; 2. purified vitronectin (positive control); 3. rat lens capsule (with adherent epithelial cells) lysate. H-K: In situ hybridization for vitronectin in rat eyes. H: At E12.5, mRNA for vitronectin is expressed in both primary fibers and differentiating epithelium. I: at E17.5, vitronectin mRNA is present in the epithelium but weaker in the most mature primary fibers. J: At P7, vitronectin mRNA is predominantly expressed in the epithelium and transitional zone and little or no signal is detected in the fibers. K: at P21 vitronectin expression is similar to that at P7. Abbreviations are: ca; capsule; epi, epithelium; f, fibers; pf, primary fibers; tz, transitional zone. The scale bar indicates 100 μm in J and K, 40 μm in I, and 20 μm in A-F, and H.