![]() Figure 1 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2006;
12:937-948.
Figure 1 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2006;
12:937-948.
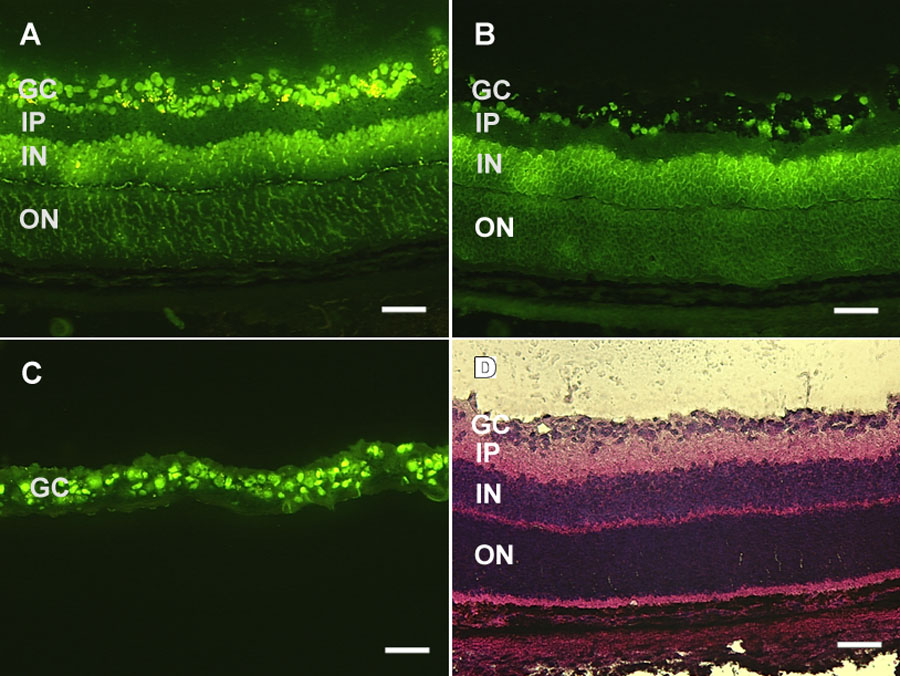
Figure 1. Visualization of retinal ganglion cells and LCM
Retinal ganglion cells were retrograde labeled by injection of the fluorescent dye aminostilbamidine into the superior colliculus and visualized using fluorescent microscopy. A: The retinal ganglion cells are in the upper most fluorescent layer, with round cell bodies exhibiting a strong fluorescence. Background fluorescence allows the inner and outer nuclear layers to be distinguished. B: The same section as shown in A, after LCM. Most of the ganglion cells have been removed while the underlying inner nuclear cell layer is unperturbed. C: The post-LCM ganglion cells adhering to the underside of the capturing cap. D: HE staining of a retinal cryosection from the same rat pup. The scale bar represents 50 μm. The ganglion cell layer (GC), inner plexiform layer (IP), inner nuclear layer (IN), and outer nuclear layer (ON) are indentified.