![]() Figure 6 of
Mader, Mol Vis 2006;
12:915-930.
Figure 6 of
Mader, Mol Vis 2006;
12:915-930.
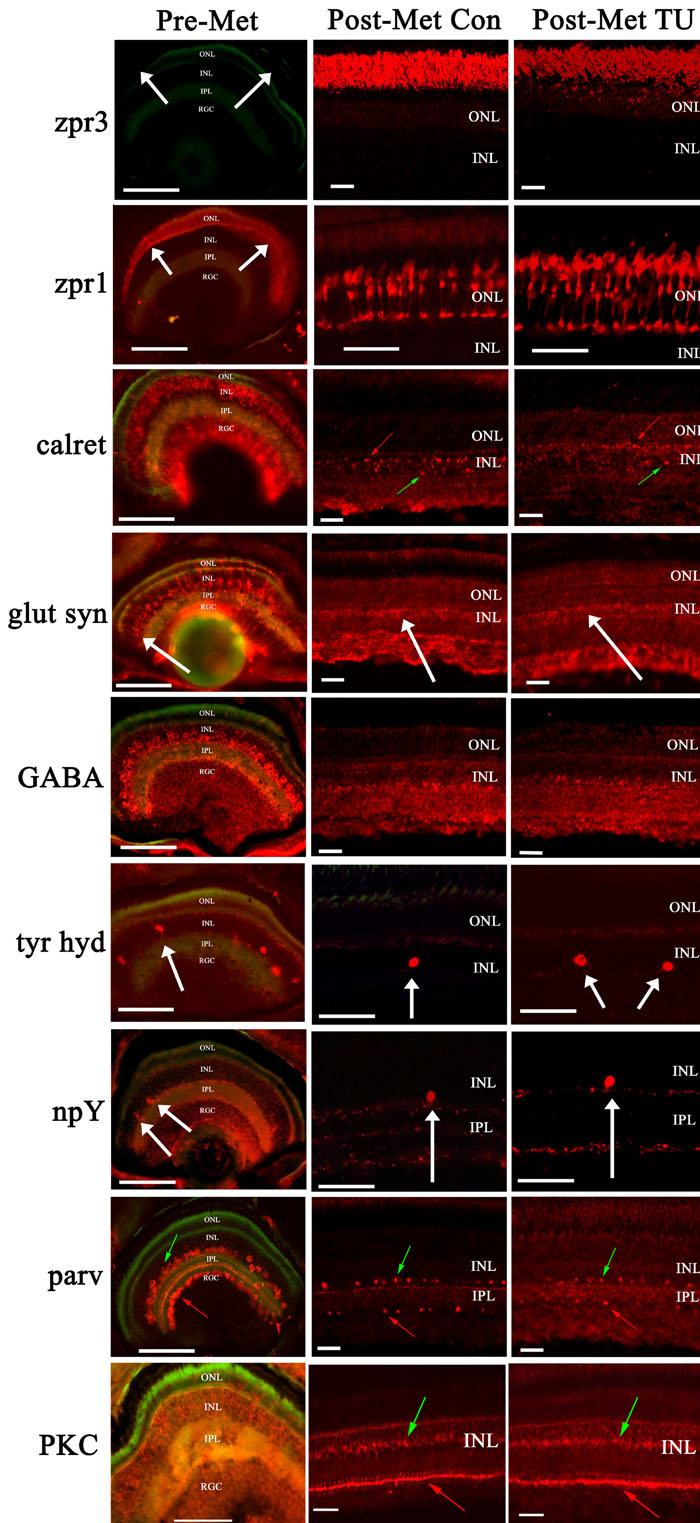
Figure 6. Retinal cell types in flounder retina
The condition/source of the displayed cryosections is indicated along the top of each column, and the identity of the screened primary antibody is indicated to the left of each row. Zpr3, a rod marker, labels rod outer segments in control and hypothyroidic postmetamorphic retina, but is absent from the corresponding region of premetamorphic retina (white arrows). Zpr1, a cone marker, is present in premetamorphic retina (white arrows) and both postmetamorphic conditions. In all conditions anti-calretinin (calret) labels a set of apparent horizontal (red arrow) and amacrine cells (green arrow). Anti-glutamine synthetase (glut syn) labels Müller glia in all conditions, with the somata indicated by white arrows. Anti-gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) labels retinal cells in the INL and RGC of all conditions, likely including examples of horizontal, amacrine, and retinal ganglion cells [48]. Anti-tyrosine hydroxylase (tyr hyd) labels a subclass of cells with relatively large soma (white arrows) at the INL/IPL boundary in all conditions. Anti-neuropeptide Y (npY) labels a relatively rare subclass of cell with somata located in the INL in all conditions (white arrows). In all conditions anti-parvalbumin (parv) apparently labels a set of amacrine cells (green arrows) and cells in the RGC layer (red arrows). An antibody against protein kinase C (PKC) apparently labels ON-type bipolar cells in all conditions, with the somata (green arrows) and synaptic end feet (red arrows) indicated. In all panels, the scale bar represents 50 μm.