![]() Figure 1 of
van den Hurk, Mol Vis 2005;
11:263-273.
Figure 1 of
van den Hurk, Mol Vis 2005;
11:263-273.
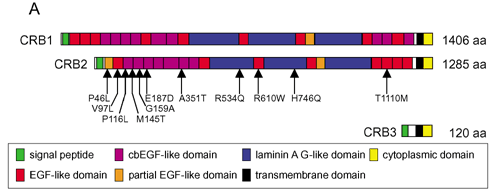
Figure 1. Comparison of the CRB1, CRB2 and CRB3 proteins
A: The protein domain structures of CRB1, CRB2, and CRB3. CRB1 and CRB2 contain a large extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and a 37 amino acid cytoplasmic domain. CRB3 lacks the extracellular domain, but has a cytoplasmic domain that is highly similar to CRB1 and CRB2. Amino acid substitutions found in the CRB2 gene in RP and LCA patients are indicated by arrows. Numbering is based on GenBank entry AY720432. B: Alignment of the cytoplasmic domains of Drosophila (Dm) Crumbs (CRB; M33753), human (Hs) CRB1 (AY043325), human (Hs) CRB2 (AY720432), and human (Hs) CRB3 (AY103469). Identical amino acids are indicated in red and conserved residues in blue. Each line lists the organism, protein name, N-terminal amino acid position of the cytoplasmic domain, amino acid sequence of the cytoplasmic domain, and C-terminal amino acid position of the cytoplasmic domain. Asterisks mark the stop codons.
B:
Dm CRB 2110 RNKRATRGTYSPSAQEYCNPRLEMDNVLKPPPEERLI* 2146 Hs CRB1 1370 SNKRATQGTYSPSRQEKEGSRVEMWNLMPPPAMERLI* 1406 Hs CRB2 1249 RKRRQSEGTYSPSQQEVAGARLEMDSVLKVPPEERLI* 1285 Hs CRB3 84 REKRQTEGTYRPSSEEQVGARVPPTPNLKLPPEERLI* 120 |