![]() Figure 5 of
Kraft, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1246-1256.
Figure 5 of
Kraft, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1246-1256.
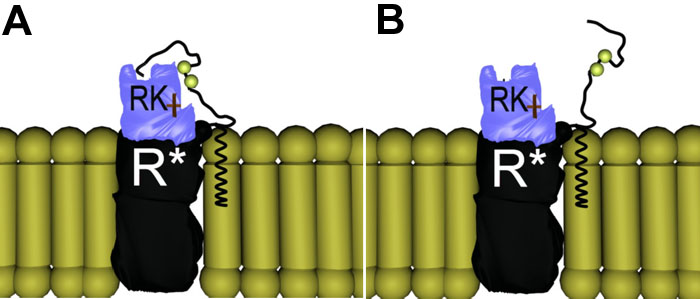
Figure 5. The Proline Hook Model of the phosphorylation of photoisomerized rhodopsin by rhodopsin kinase
The "proline hook" model of the phosphorylation of photoisomerized rhodopsin (R*) by rhodopsin kinase (RK) incorporates the idea that the proline residue in position 347 creates a hook at the very carboxy terminus of rhodopsin, and that there is a binding site for this hook on RK. A: Wild type rhodopsin is phosphorylated rapidly and reproducibly because the carboxy terminus is tethered at both ends, reducing the range of motion and dramatically increasing the probability of interactions of the serine and threonine residues with the catalytic site of RK. B: ADRP-causing mutations without the proline hook are still capable of the multiple and complete phosphorylation, but because of the increased mobility of the carboxy terminus, phosphorylation time (lifetime of R*) is longer and much more variable.