![]() Figure 4 of
Shimauchi-Matsukawa, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1220-1228.
Figure 4 of
Shimauchi-Matsukawa, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1220-1228.
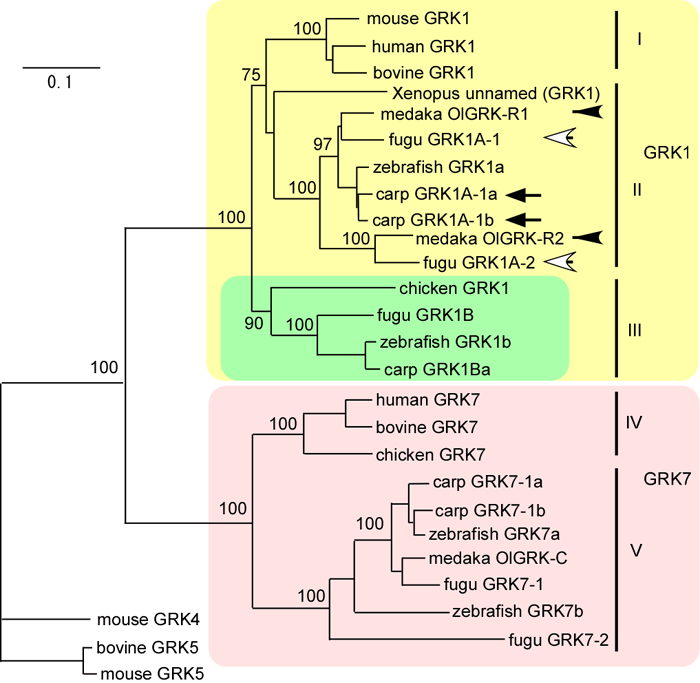
Figure 4. Molecular phylogenic tree of vertebrate GRK genes
This tree was constructed by comparison of 312 amino acid residues of GRK by the neighbor-joining method. The numbers at the branches are bootstrap values that indicate confidence in the topology of the tree. This method produces an unrooted tree. However, we confirmed the root position by using mouse GRK4, GRK5, and bovine GRK5 as outgroups. Branch length is proportional to the number for amino acid substitutions; the scale bar represents 0.1 amino acid substitutions per position in the sequences. GenBank accession numbers: mouse GRK1 (AAD40189), GRK4 (AAC09266), GRK5 (AAC09267), bovine GRK1 (AAA30752), GRK5 (AAA17561), GRK7 (AAL06241), human GRK1 (NP_002920), GRK7 (AAL48216), chicken GRK1 (AAC08428), GRK7 (XP_426681), medaka OlGRK-R (BAA25671), OlGRK-C (BAA25670), zebrafish GRK1a (AAX69079), GRK1b (AAX69080), GRK7a (AAX69081), GRK7b (AAX69082), Xenopus unnamed (GRK1; AAH94133). Fugu GRK homologs were identified using carp GRKs as query sequences in the predicted protein database of NCBI: fugu GRK1A-1 (SINFRUP00000068890), GRK1A-2 (SINFRUP00000069492), GRK1B (SINFRUP00000090819), GRK7-1 (SINFRUP00000074019), GRK7-2 (SINFRUP00000079637).