![]() Figure 8 of
Nguyen, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1183-1199.
Figure 8 of
Nguyen, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1183-1199.
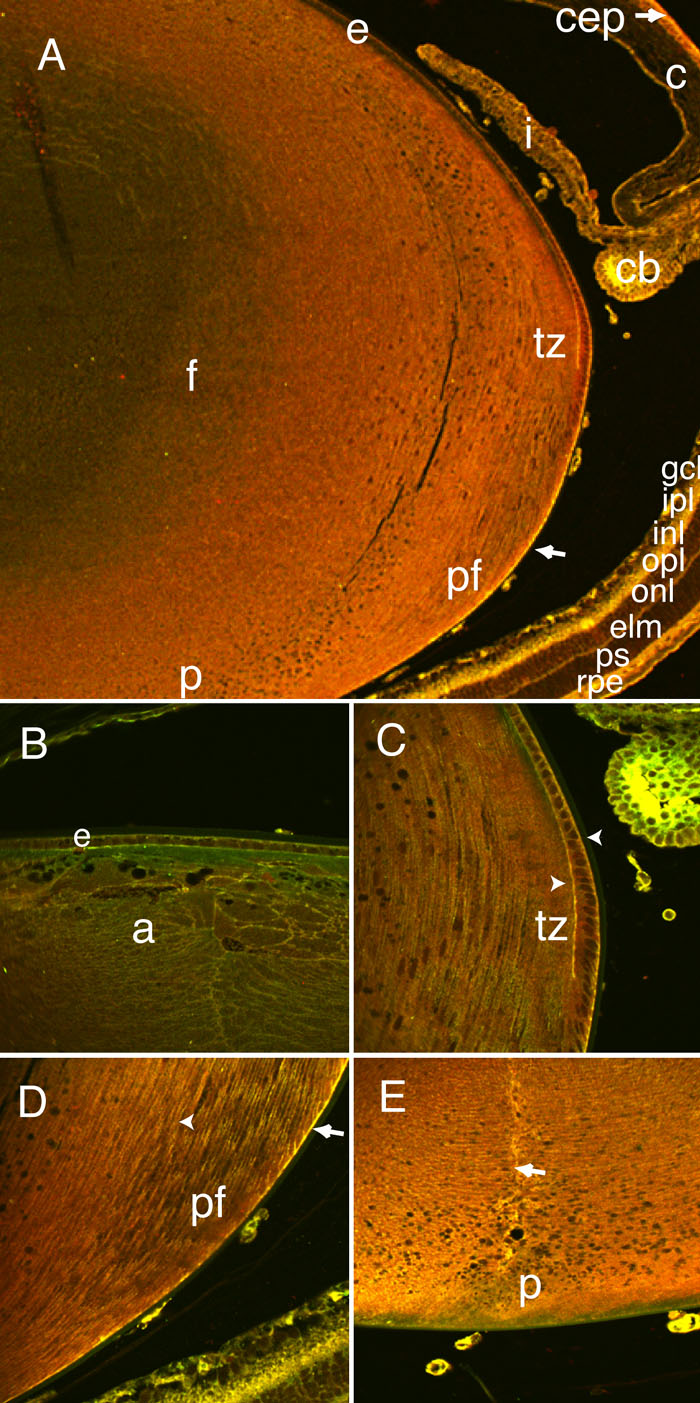
Figure 8. Co-localization of Dlg-1 and Scrib in the eye
To determine where Dlg-1 and Scrib co-localized in the eye, we conducted double immunofluorescence experiments on eye sections from P10 mice. Extensive overlap of Dlg-1 and Scrib was observed throughout the eye. Lower magnification of lens epithelium (e; A), higher magnification of lens epithelium (B), lens transition zone (tz) and ciliary body (C), lens posterior fibers and retina (r; D), and lens posterior (E). Staining for Dlg-1 is red, staining for Scrib is green and overlap in staining for Dlg-1 and Scrib is yellow. The arrows in A,D show overlap in Dlg-1 and Scrib staining along the basal edge of the posterior fiber cells at the capsule. The arrowheads in C show overlap in staining on the basal surface of the lens epithelial cells and the apical-apical interface of the epithelial and fiber cells. The arrowhead in D shows overlap on the lateral surfaces of the fibers in the posterior region. The arrow in E shows the strong overlap of Dlg-1 and Scrib staining along the posterior suture of the lens. Overlap in staining of Dlg-1 and Scrib also was observed in the corneal epithelium (cep; A, arrow), the iris (i; A), the inner epithelium of the ciliary body (cb; A,C), and the ganglion cell layer (gcl), outer plexiform layer (opl), external limiting membrane (elm), and retinal pigment epithelium (rpe) of the retina (A). The anterior (apical) region of lens fibers (a), cornea (c), lens fiber cells (f), midposterior fibers (pf), and posterior (p) are identified. In all panels, the anterior of the eye is oriented at the top.