![]() Figure 5 of
Houdart, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1061-1070.
Figure 5 of
Houdart, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1061-1070.
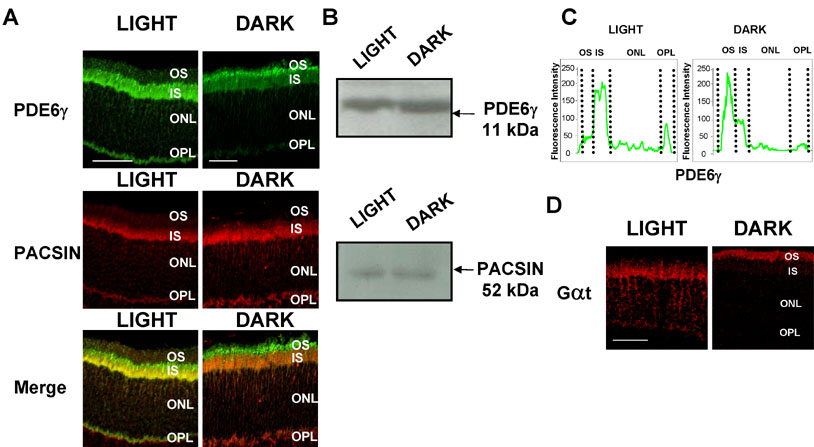
Figure 5. Expression and immunolocalization of PDE6γ and PACSIN in dark and light adapted retinas
A: PDE6γ and PACSIN were detected in cross-sections of dark- or light-adapted retinas by immunofluorescence staining. Eyes were fixed in Bouin's fixative and embedded in paraffin. Tissue sections (12 μm) were incubated overnight at 4 °C with a mix of anti-PDE6γ (1:10,000) and anti-PACSIN (1:250) antibodies, then for 1 h with a mix of Alexa488-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:200, green fluorescence for PDE6γ) and Alexa568-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (1:200, red fluorescence for PACSIN). Upon retina illumination, PDE6γ translocates to photoreceptor inner segments and synapses. PACSIN is localized in inner segments and synapses in both conditions. PDE6γ-PACSIN colocalization in inner segments and synapses layers of photoreceptors increased in light conditions (scale bar indicates 40 μm). B: Western blot analysis of PDE6γ and PACSIN expression under dark and light conditions: Extracts of light or dark adapted retinas were homogenized in Laemmli sample buffer (3 μg protein/μl) and 60 μg were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blot. Ponceau red staining of the western blots was used to verify equal protein loading. C: Fluorescence intensity of PDE6γ labeling in different layers of dark- and light-adapted retinas. PDE6γ translocates from outer to inner segments and outer plexiform layer upon retina illumination. D: Immunofluorescence detection of transducin, GaT, in photoreceptors of dark- and light-adapted retinas as a control (the scale bar represents 40 μm). Tissue sections (12 μm in thickness) were incubated overnight at 4 °C with an anti-GaT antibody (1:500), then for 1 h with an Alexa568-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (1:200, red fluorescence). Retinal layers are abbreviated as follows: OS represents outer segments; IS represents inner segments; ONL represents outer nuclear layer; and OPL represents outer plexiform layer.