![]() Figure 5 of
Young, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1041-1051.
Figure 5 of
Young, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1041-1051.
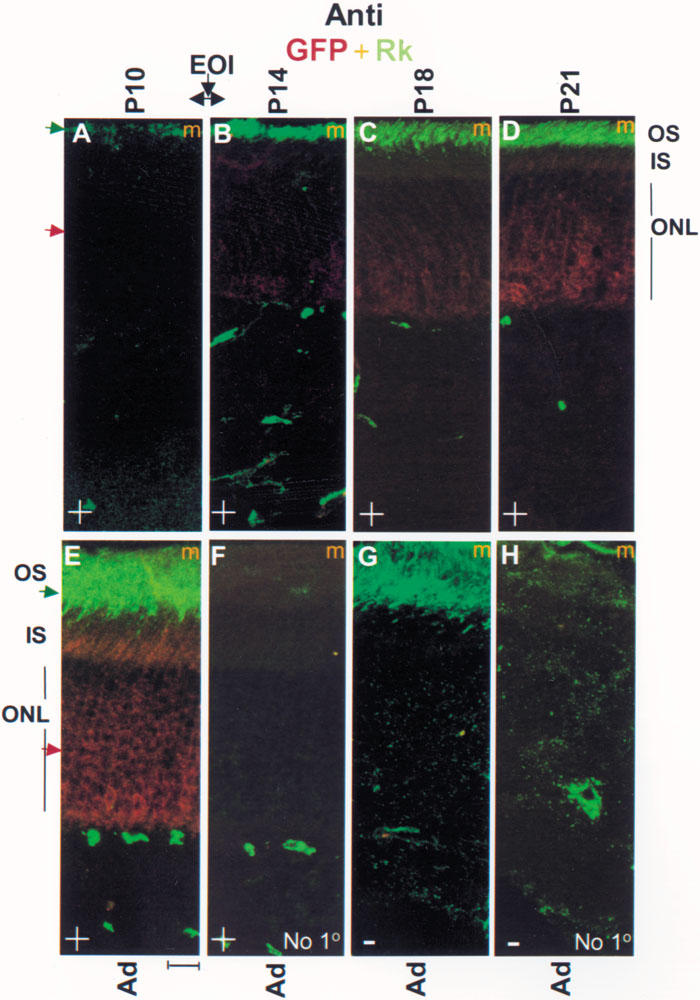
Figure 5. Parallel rhodopsin kinase (Rk) and GFP temporal expression patterns in postnatal Rk-GFP transgenic mice
Globes were harvested from transgenic mice of varying postnatal age in light-adapted state, fixed then immunostained. A-E: Merged (m) confocal micrographs of globe sections labeled with a combination of polyclonal anti-GFP (red, 1:1000) and monoclonal anti-Rk (green; 1:1000) are shown. Identical gains and laser intensities were used to scan 1 μm thick optical slices from 6 μm thick tissue sections. The central four 1 μm thick optical slices from the two channels have been stacked, projected, and merged. Comparable background fluorescence at the inner retinal layers among various panels further validate the comparison of outer segment fluorescence as a means of qualitatively gauging relative levels of GFP and Rk expression. In bright light, virtually all of Rk translocates away from cytosolic GFP to outer segments therefore allowing parallel, simultaneous monitoring of GFP and Rk expression patterns. F-H: The "no primary antibody" controls show a few spots of bright, nonspecific fluorescence in the inner layer that do not stain with anti-GFP antibody (compare E and F). Images from animals with the GFP genotype are marked with a plus "+"; others are marked with a minus "-". No differences in the content or patterns of Rk expression were detected between GFP-positive (E) and GFP-negative animals (G). At least two separate animals were examined for each time point. Scale bar represents 20 μM. The eye opening interval (EOI) occured between P10 and P14.