![]() Figure 2 of
Kumar, Mol Vis 2004;
10:445-449.
Figure 2 of
Kumar, Mol Vis 2004;
10:445-449.
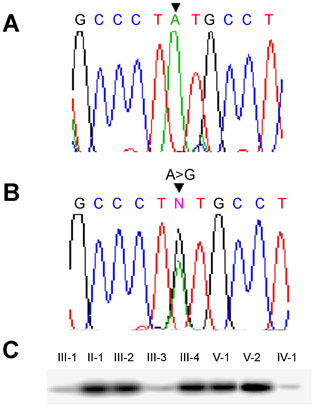
Figure 2. Mutation analysis of the FOXL2 gene
A: Sequencing chromatogram of the PCR product from normal individual IV-1. The position of the nucleotide change A->G is marked by an arrowhead. B: Sequencing chromatogram of the PCR product from affected individual III-2. Note A->G change in a heterozygous state. C: ASOH analysis of individuals from family IIS-100. Note the presence of hybridization signals in affected individuals II-1, III-2, III-4, V-1 and V-2. The blot was hybridized with the following P32-labeled mutant-allele specific oligonucleotide: 5'-CCA TGC CCT GTG CCT CCT GCC-3'. The G residue in red represents the changed nucleotide. D: Conservation of the tyrosine residue at amino acid position 215 in different orthologs of the FOXL2 gene. The position of the tyrosine residue is marked by an arrow. Note the absence of the polyalanine domain in Fugu.
D:
215
|
Human (NP_075555) PPSPMPYASCQMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAGP
Mouse (AAN04088) PPSPMPYASCQMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAGP
Goat (AAM52099) PPSPMPYASCQMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAGP
Rat (XP_345976) PPSPMPYASCQMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAGP
Rabbit (AAQ91846) PPSPMPYASCQMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAGP
Cow (AAQ91844) PPSPMPYASCQMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAGP
Pig (AA91845) PPSPMPYASCQMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAGP
Fugu (scaffold_8165) PPAPMSYTSCQMAS------------GN
|