![]() Figure 8 of
Ottino, Mol Vis 2004;
10:341-350.
Figure 8 of
Ottino, Mol Vis 2004;
10:341-350.
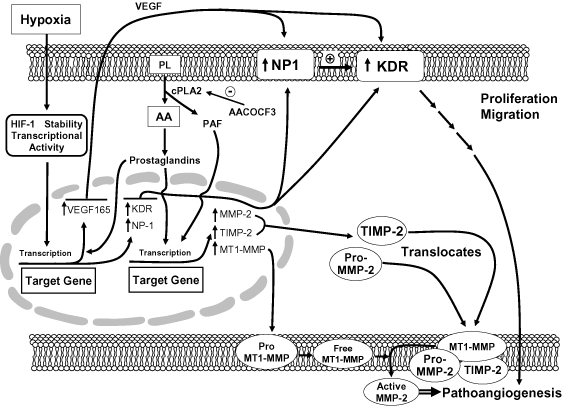
Figure 8. Hypoxia-mediated induction of genes and lipid signaling in pathoangiogenesis in choroid-retinal EC
Hypoxia promotes binding to target genes of HIF-1αheterodimer subunit, resulting in the induction of downstream genes [23]. Hypoxia also triggers arachidonic acid (AA) release and prostaglandin and platelet-activating factor synthesis via cPLA2. In addition, hypoxia induces VEGF-165, KDR, and NP-1 receptor expression. NP-1 increases the affinity of VEGF-165 for KDR receptor and contributes as part of an autocrine loop to neovascularization. This outline depicts selective induction of MT1-MMP, MMP-2, and TIMP-2 and the stepwise activation of the pro-MMP-2 enzyme by TIMP-2 and MT1-MMP binding at the membrane surface. Activation of MMP-2 leads to neovascularization. The inhibition of cPLA2 decreases VEGF-165 release and MMP induction, in turn reducing microtubule formation.