![]() Figure 1 of
Fischer, Mol Vis 2004;
10:973-986.
Figure 1 of
Fischer, Mol Vis 2004;
10:973-986.
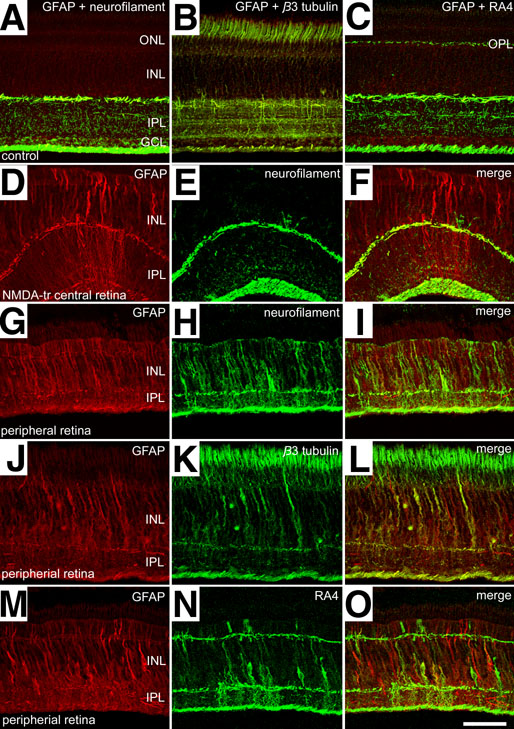
Figure 1. Retinal damage induces glial expression of filamentous proteins
NMDA induced retinal damage causes Müller glia to become immunoreactive for GFAP, neurofilament, β3 tubulin, and RA4. Retinal sections were obtained from eyes 3 days after treatment with saline (A-C) or NMDA (D-O). Sections were labeled with antibodies to GFAP and neurofilament (NF-M; A,D-I), GFAP and β3 tubulin (B,J-L), or GFAP and RA4 (C,M-O). Images were taken from central (A-F) or peripheral (G-O) regions of the retina. Confocal images were obtained by projecting 7 optical sections that were 1.2 μm in thickness. For all images, identical settings were used on the microscope and for post-acquisition processing to maintain the relative labeling intensity. The calibration bar in O represents 50 μm and applies to all panels. The outer nuclear layer (ONL), inner nuclear layer (INL), inner plexiform layer (IPL), and ganglion cell layer (GCL) are labeled.