![]() Figure 2 of
Dejneka, Mol Vis 2004;
10:964-972.
Figure 2 of
Dejneka, Mol Vis 2004;
10:964-972.
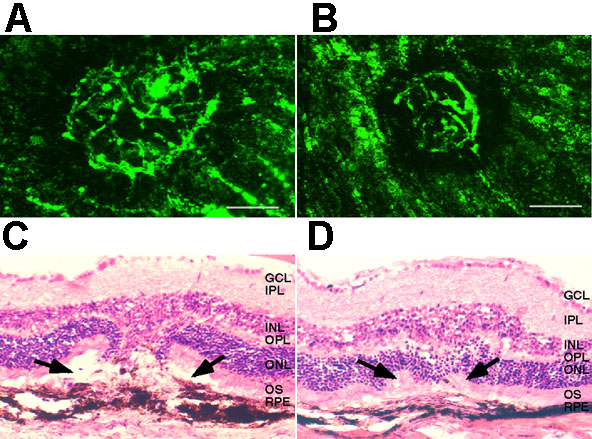
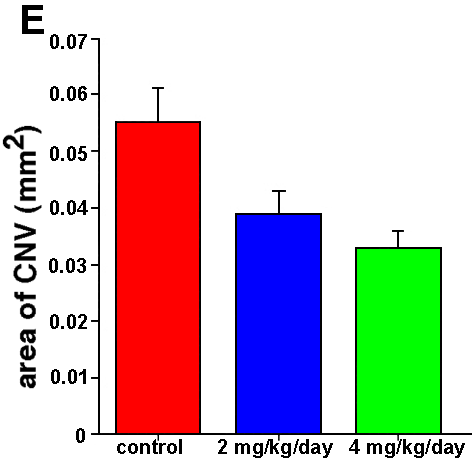
Figure 2. Rapamycin significantly reduces laser induced choroidal neovascularization
Fluorescein dextran choroidal flat mounts of PBS (A) and rapamycin treated (4 mg/kg/day, B) animals. Representative cryopreserved histological sections (20x), stained with hematoxylin and eosin, are shown below (C,D). Arrows highlight the difference in the size of the lesioned area with (4 mg/kg/day, D) and without (PBS, C) rapamycin treatment. Scale bar represents 200 μm. A 29.8% and 40% reduction in the area of CNV was observed following low and high dose rapamycin administration, respectively (E). The error bars represent SEM.