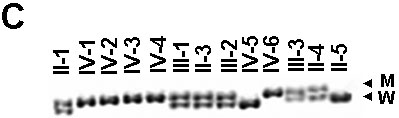![]() Figure 2 of
Kumar, Mol Vis 2004;
10:910-916.
Figure 2 of
Kumar, Mol Vis 2004;
10:910-916.
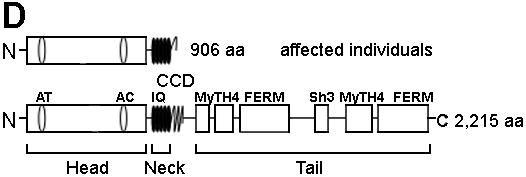
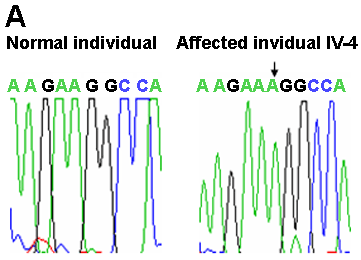
Figure 2. Mutation analysis of the MYO7A gene in the family
A: Sequencing chromatograms of PCR products of exon 22 from a normal individual and the affected individual IV-4; insertion of an A residue is marked by an arrow. B: Partial nucleotide and amino acid sequences of wild type (normal) and mutant alleles; insertion site of an A residue is marked above by a "pipe" (|) in the wild type allele; a missense run of 18 amino acids are shown in purple in the mutant protein; premature stop codon in exon 23 is shown in red. C: PCR-SSCP analysis of all 13 individuals from the family, note all five affected individuals (IV-1, IV-2, IV-3, IV-4, and IV-6) are homozygous for the mutant allele (M) and their parents (II-1, III-1, III-2, and III-3) are heterozygous for the mutant and the wild type (W) alleles. D: Schematic representation of mutant (above) and normal MYO7A (below) proteins. Note the truncation of MYO7A protein in affected individuals. The normal protein has a head domain with an ATP binding site (AT) and an actin binding site (AC), followed by a neck region with isoleucine glutamine motifs (IQ), a short coiled-coil domain (CCD), and a tail region with myosine tail homology 4 (MyTH4) domain, 4.1 protein ezerin-radixin-moesin-like domain (FERM) and src homology type 3 (SH3) domain.
B:
Wild type MYO7A
Exon 22
|
2656 GCC AAG AAG GCC AAG GAG GAG GCC GAG CGC AAG CAT
886 A K K A K E E A E R K H
Exon 23
CAG GAG CGC CTG GCC CAG CTG GCT CGT GAG GAC
Q E R L A E L A R E D
Mutant MYO7A
GCC AAG AAA GGC CAA GGA GGA GGC CGA GCG CAA GCA
A K K G Q G G G R A Q A
TCA GGA GCG CCT GGC CCA GCT GGC TCG TGA GGA C
S G A P G P A G S
|