![]() Figure 1 of
Cornish, Mol Vis 2004;
10:1-14.
Figure 1 of
Cornish, Mol Vis 2004;
10:1-14.
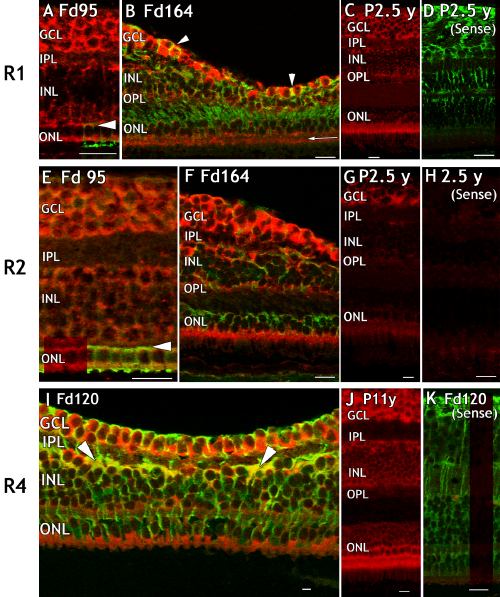
Figure 1. Distribution of FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 mRNAs in fetal and postnatal monkey retina
Developmental series of macaque retinal sections hybridized using rat RNA probes to show expression of FGFR1 (A-D) and FGFR2 (E-H) mRNA (red); and FGFR4 mRNA expression (I-K) using a probe designed from fetal human PCR product. Some sections are counter-labelled (green) to show either L/M opsin (A, E) or vimentin-IR. A: The incipient fovea, showing cytoplasmic FGFR1 mRNA expression in all cellular layers and in L/M opsin-IR cones. Horizontal arrowhead (A, E) indicates the position of the developing outer plexiform layer. B: Intense FGFR1 mRNA expression in the cytoplasm of foveal ganglion cells (red) and the end feet of MC, which are also vimentin-IR (yellow, arrowheads). FGFR1 mRNA is also detected on the outer aspect of the cone photoreceptor nuclei and in the adjoining inner segment, separated by the external limiting membrane (horizontal arrow). C: FGFR1 mRNA is low in the INL in postnatal retina. D: FGFR1 sense probe hybridized to adult retina, counter labelled with anti-vimentin (green). E: FGFR2 in all cell layers at the incipient fovea including L/M opsin-IR cones. F: Intense FGFR2 expression in the GCL, inner segments of cones and inner and outer aspects of the INL, during formation of the foveal depression. G: FGFR2 expression is high in the GCL in postnatal retina but low in the INL and ONL. H: FGFR2 sense probe. I: Co-localization of FGFR4 with vimentin-IR Müller cells (yellow, arrowheads). Cones express abundant FGFR4 mRNA. J: FGFR4 expression is strongest in the GCL and ONL in adult retina. K: FGFR4 sense probe, immunolabelled with anti-vimentin. All scale bars represent 20 μm. The ganglion cell layer (GCL), inner nuclear layer (INL), inner plexiform layer (IPL), and outer nuclear layer (ONL) are also identified.