 Return to Bernstein et al
Return to Bernstein et al
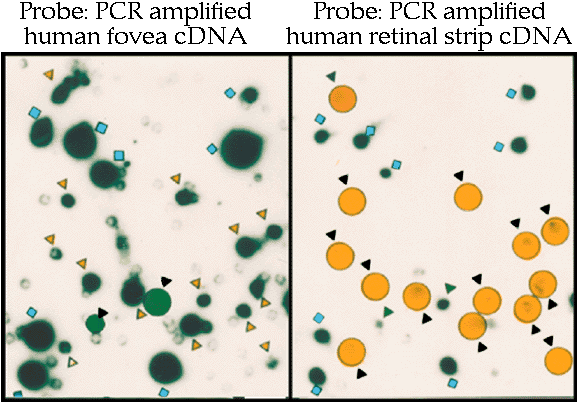
Panel A) Primary screening The two panels show duplicate plaque lifts screened with a mixed cDNA probe derived from either human fovea (left panel) or midperipheral retina poly(A+)RNA (right panel). Clones generating roughly equivalent signals when probed with cDNA probes from both human fovea and midperipheral retina are indicated by blue squares. Clones generating stronger signals when screened with the fovea cDNA probe are indicated by either yellow circles in the autoradiograph of the blot probed with the foveal cDNA probe or yellow triangles in the duplicate blot probed with midperipheral retina cDNA probe. Alternatively, clones producing stronger signals when reacted with the midperipheral retina cDNA probe than with the foveal cDNA probe are indicated by green circles and triangles, respectively. In total 411 putative differential fovea clones were isolated.
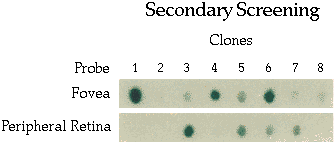
Panel B) Secondary screening of putative differential fovea clones. The cDNA insert from each clone isolated above was PCR amplified and spotted onto duplicate nylon membranes (secondary blots). One membrane was screened with the mixed fovea cDNA probe and the duplicate blot was probed wiht the mixed midperipheral retina cDNA probe. Clones which which showed a differential fovea expression pattern (columns 1, 2, 4, 6, 8) were kept for further analysis. Clones, which upon secondary screening that did not show higher relative levels of hybridization with the fovea cDNA probe, were removed from further analysis (columns 3, 5, 7).
 Return to Bernstein et al
Return to Bernstein et al